Bacterial Flora Associated with Diseased Freshwater Ornamental Fish
- PMID: 29978108
- PMCID: PMC5937343
- DOI: 10.1515/jvetres-2017-0070
Bacterial Flora Associated with Diseased Freshwater Ornamental Fish
Abstract
Introduction: Ornamental fish can suffer from different bacterial diseases. Among them the most prevalent are infections caused by Aeromonas, Shewanella, Citrobacter, Plesiomonas, Edwardsiella, and Pseudomonas. But there is a broad spectrum of rarely identified bacteria which may be causative agents of diseases. The aim of the study was to determine the species of bacteria pathogenic for fish which are prevalent in aquariums.
Material and methods: Bacteria were isolated from infected ornamental fish from pet shops and private aquariums in the Lublin region in 2015 and classified to species using MALDI-TOF MS.
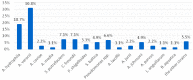
Results: A total of 182 isolates from ornamental fish were identified. The most frequent bacteria found in diseased fish were Aeromonas veronii (30.8% of total number of strains), A. hydrophila (18.7%), Shewanella putrefaciens (7.1%), Citrobacter freundii (7.1%), Pseudomonas spp. (7.1%), Shewanella baltica (4.9%), and Plesiomonas shigelloides (3.3%).
Conclusion: Isolated bacterial species are facultative pathogens for fish and humans and may be isolated from fish without apparent symptoms of the disease.
Keywords: MALDI-TOF MS method; fish pathogens; ornamental fish; species identification.
Figures
References
-
- Altun S., Büyükekiz A.G., Duman M., Özyiğit Ö., Karatas S., Turgay E.. Isolation of Shewanella putrefaciens from goldfish (Carassius auratus auratus) Isr J Aquacult-Bamid. 2014;66:956–962.
-
- Berthe F.C.J., Michel C., Bernadet J.F.. Identification of Pseudomonas anguilliseptica isolated from several fish species in France. Dis Aquat Org. 1995;21:151–155.
-
- Bhadra B., Roy P., Chakraborty R.. Serratia ureilytica sp. nov., a novel urea-utilizing species. Int J Syst Evol Micr. 2005;55:2155–2158. - PubMed
-
- Blazer V.S., Shotts E.B., Waltman W.D.. Pathology associated with Edwardsiella ictaluri in catfish Ictalurus punctatus Rafinesque, and Danio devario (Hamilton-Buchanan, 1822) J Fish Biol. 1985;27:167–175.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
