Ogilvie's syndrome: management and outcomes
- PMID: 29979381
- PMCID: PMC6076157
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011187
Ogilvie's syndrome: management and outcomes
Abstract
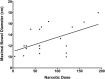
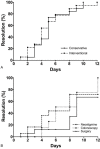
Ogilvie's syndrome, also known as acute colonic pseudo-obstruction, refers to pathologic dilation of the colon without underlying mechanical obstruction, occurring primarily in patients with serious comorbidities. Diagnosis of Ogilvie's syndrome is based on clinical and radiologic grounds, and can be treated conservatively or with interventions such as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (such as neostigmine), decompressive procedures including colonoscopy, and even surgery. Based on our clinical experience we hypothesized that conservative management yields similar, if not superior, results to interventional management. Therefore, we retrospectively examined all patients over the age of 18 with Ogilvie's syndrome who presented to the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC). The diagnosis of Ogilvie's syndrome was confirmed by clinical criteria, including imaging evidence of colonic dilation ≥9 cm. Patients were divided and analyzed in 2 groups based on management: conservative (observation, rectal tube, nasogastric tube, fluid resuscitation, and correction of electrolytes) and interventional (neostigmine, colonoscopy, and surgery). Use of narcotics in relation to maximal bowel size was also analyzed. Over the 11-year study period (2005-2015), 37 patients with Ogilvie's syndrome were identified. The average age was 67 years and the average maximal bowel diameter was 12.5 cm. Overall, 19 patients (51%) were managed conservatively and 18 (49%) underwent interventional management. There was no significant difference in bowel dilation (12.0 cm vs 13.0 cm; P = .21), comorbidities (based on the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), 3.2 vs 3.4; P = .74), or narcotic use (P = .79) between the conservative and interventional management groups, respectively. Of the 18 patients undergoing interventional management, 11 (61%) had Ogilvie's-syndrome-related complications compared to 4 (21%) of the 19 patients in the conservative management group (P < .01). There was no difference in overall length of stay in the 2 groups. Two patients, one in each group, died from complications unrelated to their Ogilvie's syndrome. We conclude that Ogilvie's syndrome, although uncommon, and typically associated with severe underlying disease, is currently associated with a low inpatient mortality. While interventional management is often alluded to in the literature, we found no evidence that aggressive measures lead to improved outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Kaiser AM. Ogilvie transition to colonic perforation. Am J Surg 2010;200:e15–6. - PubMed
-
- Ross SW, Oommen B, Wormer BA, et al. Acute colonic pseudo-obstruction: defining the epidemiology, treatment, and adverse outcomes of Ogilvie's syndrome. Am Surg 2016;82:102–11. - PubMed
-
- Vanek VW, Al-Salti M. Acute pseudo-obstruction of the colon (Ogilvie's syndrome). An analysis of 400 cases. Dis Colon Rectum 1986;29:203–10. - PubMed
-
- Saunders MD, Kimmey MB. Systematic review: acute colonic pseudo-obstruction. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005;22:917–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

