Etiological aspects of intragastric bezoars and its associations to the gastric function implications: A case report and a literature review
- PMID: 29979404
- PMCID: PMC6076189
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011320
Etiological aspects of intragastric bezoars and its associations to the gastric function implications: A case report and a literature review
Abstract
Rationale: Intragastric bezoar is a stony mass found trapped in the stomach, though it can occur in other locations of the gastro-intestinal tract. The etiology of intragastric bezoar is multifactorial, includes certain risk factors and predisposing factors such as coexisting medical disorders, anatomic abnormalities, and gastric motility disorders, which contribute to the development of intragastric bezoar.
Patient concerns: In this report, we present a rare case of intragastric bezoar with epigastric pain after prolonged consumption of jujubes. To our knowledge, this is the first case of intragastric bezoar to be reported after jujubes ingestion.
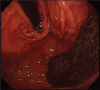
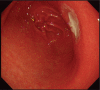
Diagnoses: An upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy performed which revealed an 8 × 5-cm intragastric diospyrobezoar with an adjacent necrotic pressure ulcer of size 0.8 × 0.5-cm without signs of bleeding.
Interventions: For therapeutic intervention, Coca-Cola ingestion and lithotripsy were applied.
Outcomes: The therapeutic course was uneventful. There was no recurrence during 1-year follow-up.
Lessons: In our literature, jujube emerged as a new player. A bezoar composed of unripened fruit content in the stomach, could be the cause of chronic abdominal pain, dyspepsia, gastric reflux or heartburn. Moreover, this study provides a detailed overview of recently published literature regarding intragastric manifestations of bezoar, etiological factors, diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Nour I, Abd Alatef M, Megahed A, et al. Rapunzel syndrome (gastric trichobezoar), a rare presentation with generalised oedema: case report and review of the literature. Paediatr Int Child Health 2017;1–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources