Diagnostic accuracy of adding copeptin to cardiac troponin for non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29979797
- PMCID: PMC6034895
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200379
Diagnostic accuracy of adding copeptin to cardiac troponin for non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: This study aimed to determine the diagnostic accuracy of adding copeptin to cardiac troponin (cTn) on admission to the emergency department (ED) for non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) compared to cTn alone.
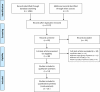
Materials and methods: A literature search of MEDLINE, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library was performed (search date: April 13, 2018). Primary studies were included if they accurately reported on patients with symptoms suggestive of acute myocardial infarction and measured both cTn alone and cTn with copeptin upon admission to the ED. The patients with evidence of ST elevation myocardial infarction were excluded. To assess the risk of bias for the included studies, the QUADAS-2 tool was used.
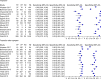
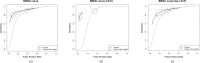
Results: The study participants included a total of 7,998 patients from 14 observational studies. The addition of copeptin to cTn significantly improved the sensitivity (0.81 [0.74 to 0.87] vs. 0.92 [0.89 to 0.95], respectively, p <0.001) and negative predictive value (0.96 [0.95 to 0.98] vs. 0.98 [0.96 to 0.99], respectively, p <0.001) at the expense of lower specificity (0.88 [0.80 to 0.97] vs. 0.57 [0.49 to 0.65], respectively, p <0.001) compared to cTn alone. Furthermore, adding copeptin to cTn showed significantly lower diagnostic accuracy for NSTEMI compared to cTn alone (0.91[0.90 to 0.92] vs. 0.85 [0.83 to 0.86], respectively, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Adding copeptin to cTn improved the sensitivity and negative predictive value for the diagnosis of NSTEMI compared to cTn alone. Thus, adding copeptin to cTn might help to screen NSTEMI early upon admission to the ED.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is high-sensitivity troponin, alone or in combination with copeptin, sensitive enough for ruling out NSTEMI in very early presenters at admission? A post hoc analysis performed in emergency departments.BMJ Open. 2019 Jun 16;9(6):e023994. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023994. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31209082 Free PMC article.
-
Copeptin with high-sensitivity cardiac troponin to rule out non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction early on: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Biochem. 2023 Feb;112:24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2022.11.009. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Clin Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36435204
-
Copeptin combined with either non-high sensitivity or high sensitivity cardiac troponin for instant rule-out of suspected non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction.Biomarkers. 2020 Dec;25(8):649-658. doi: 10.1080/1354750X.2020.1833084. Epub 2020 Oct 31. Biomarkers. 2020. PMID: 33045866
-
Gender-based differences of copeptin alone or combined with troponin for early rule-out of non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction.Am J Emerg Med. 2021 Jul;45:248-253. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.08.053. Epub 2020 Aug 21. Am J Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 33041108
-
Copeptin for the early rule-out of non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction.Int J Cardiol. 2016 Nov 15;223:797-804. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.08.304. Epub 2016 Aug 23. Int J Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27573613 Review.
Cited by
-
Copeptin in Acute Myocardial Infarction: Is There a Role in the Era of High-Sensitivity Troponins?J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025 Apr 9;12(4):144. doi: 10.3390/jcdd12040144. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025. PMID: 40278203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Performance of Copeptin for Early Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction in an Emergency Department Setting.Ann Lab Med. 2020 Jan;40(1):7-14. doi: 10.3343/alm.2020.40.1.7. Ann Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 31432633 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of Copeptin.Clin Biochem Rev. 2021 Feb;42(1):17-25. doi: 10.33176/AACB-20-00001. Clin Biochem Rev. 2021. PMID: 35722630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serial high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T measurements to rule out acute myocardial infarction and a single high baseline measurement for swift rule-in: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2020 Feb;9(1):14-22. doi: 10.1177/2048872618819421. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2020. PMID: 30618277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Simoons ML, Chaitman BR, White HD, et al. Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2012;126:2020–2035. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31826e1058 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hamm CW, Bassand JP, Agewall S, Bax J, Boersma E, Bueno H, et al. ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation: the Task Force for the management of acute coronary syndromes (ACS) in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2011; 32: 2999–3054. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr236 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kumar A, Cannon CP. Acute coronary syndromes: diagnosis and management, part I. Mayo Clin Proc. 2009;84:917–938. doi: 10.1016/S0025-6196(11)60509-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Raskovalova T, Twerenbold R, Collinson PO, Keller T, Bouvaist H, Folli C, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of combined cardiac troponin and copeptin assessment for early rule-out of myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 2014;3:18–27. doi: 10.1177/2048872613514015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Holwerda DA. A glycopeptide from the posterior lobe of pig pituitaries. I. Isolation and characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1972;28:334–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

