Single-Cell Transcriptomics of a Human Kidney Allograft Biopsy Specimen Defines a Diverse Inflammatory Response
- PMID: 29980650
- PMCID: PMC6065085
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2018020125
Single-Cell Transcriptomics of a Human Kidney Allograft Biopsy Specimen Defines a Diverse Inflammatory Response
Abstract
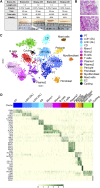
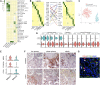
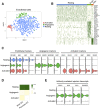
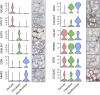
Background Single-cell genomics techniques are revolutionizing our ability to characterize complex tissues. By contrast, the techniques used to analyze renal biopsy specimens have changed little over several decades. We tested the hypothesis that single-cell RNA-sequencing can comprehensively describe cell types and states in a human kidney biopsy specimen.Methods We generated 8746 single-cell transcriptomes from a healthy adult kidney and a single kidney transplant biopsy core by single-cell RNA-sequencing. Unsupervised clustering analysis of the biopsy specimen was performed to identify 16 distinct cell types, including all of the major immune cell types and most native kidney cell types, in this biopsy specimen, for which the histologic read was mixed rejection.Results Monocytes formed two subclusters representing a nonclassical CD16+ group and a classic CD16- group expressing dendritic cell maturation markers. The presence of both monocyte cell subtypes was validated by staining of independent transplant biopsy specimens. Comparison of healthy kidney epithelial transcriptomes with biopsy specimen counterparts identified novel segment-specific proinflammatory responses in rejection. Endothelial cells formed three distinct subclusters: resting cells and two activated endothelial cell groups. One activated endothelial cell group expressed Fc receptor pathway activation and Ig internalization genes, consistent with the pathologic diagnosis of antibody-mediated rejection. We mapped previously defined genes that associate with rejection outcomes to single cell types and generated a searchable online gene expression database.Conclusions We present the first step toward incorporation of single-cell transcriptomics into kidney biopsy specimen interpretation, describe a heterogeneous immune response in mixed rejection, and provide a searchable resource for the scientific community.
Keywords: kidney biopsy; rejection; transcriptional profiling.
Copyright © 2018 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures



Comment in
-
Single-cell analysis of a biopsy sample.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018 Oct;14(10):598. doi: 10.1038/s41581-018-0045-z. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30030489 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sellarés J, de Freitas DG, Mengel M, Reeve J, Einecke G, Sis B, et al.: Understanding the causes of kidney transplant failure: The dominant role of antibody-mediated rejection and nonadherence. Am J Transplant 12: 388–399, 2012 - PubMed
-
- El-Zoghby ZM, Stegall MD, Lager DJ, Kremers WK, Amer H, Gloor JM, et al.: Identifying specific causes of kidney allograft loss. Am J Transplant 9: 527–535, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Gaston RS, Cecka JM, Kasiske BL, Fieberg AM, Leduc R, Cosio FC, et al.: Evidence for antibody-mediated injury as a major determinant of late kidney allograft failure. Transplantation 90: 68–74, 2010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

