Antigenic characteristics and genomic analysis of novel EV-A90 enteroviruses isolated in Xinjiang, China
- PMID: 29980696
- PMCID: PMC6035207
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-28469-9
Antigenic characteristics and genomic analysis of novel EV-A90 enteroviruses isolated in Xinjiang, China
Abstract
Enterovirus A90 (EV-A90) is a novel serotype of enterovirus A species that is rarely reported. Here, we isolated five enteroviruses from patients with acute flaccid paralysis in Hotan and Kashgar cities in Xinjiang, China that were identified as EV-A90 by molecular typing. The VP1 sequences of these Xinjiang EV-A90 strains showed 88.4-89% nucleotide sequence identity to the prototype EV-A90 strain; however, genome analysis indicated complex recombination events in P2 and P3 regions. Next, the seroprevalence of EV-A90 was examined in 49 serum specimens collected in Hotan and Kashgar, and 37.5% were EV-A90 antibody positive (>1:8), with a geometric mean titre (GMT) of 1:10.47. The low positive rate and GMT suggest a low-level EV-A90 epidemic in Xinjiang. Two of the five Xinjiang EV-A90 strains were temperature sensitive, and three were temperature resistant, and a comparative genomics analysis suggested that an amino acid substitution (H1799Y) in the 3Dpol region was related to temperature sensitivity. Although the epidemic strength is low, some EV-A90 strains were temperature resistant, which is suggestive of strong virulence and transmission capacity. This study expanded the number of EV-A90 in GenBank and provided basic data that may be useful for studying the molecular epidemiology of EV-A90.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

 and the prototype of EV-A90 (BAN00-10399) was marked with
and the prototype of EV-A90 (BAN00-10399) was marked with  . The phylogenetic tree was reconstructed using neighbor-joining method with the substitution model of maximum composite likelihood model.
. The phylogenetic tree was reconstructed using neighbor-joining method with the substitution model of maximum composite likelihood model.
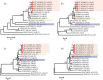
 and the prototype of EV-A90 (BAN00-10399) was marked with
and the prototype of EV-A90 (BAN00-10399) was marked with  . The phylogenetic tree was reconstructed using maximum likelihood method, in which GTR + I + G model was used in P1 fragment and TN93 + I + G model was used in the rest fragment. We also put forward a hypothesis between the major parental type (yellow) and the minor parental type (blue) because of recombination.
. The phylogenetic tree was reconstructed using maximum likelihood method, in which GTR + I + G model was used in P1 fragment and TN93 + I + G model was used in the rest fragment. We also put forward a hypothesis between the major parental type (yellow) and the minor parental type (blue) because of recombination.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

