How useful are hemoglobin concentration and its variations to predict significant hemorrhage in the early phase of trauma? A multicentric cohort study
- PMID: 29980953
- PMCID: PMC6035120
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-018-0420-8
How useful are hemoglobin concentration and its variations to predict significant hemorrhage in the early phase of trauma? A multicentric cohort study
Abstract
Background: The diagnostic value of hemoglobin (Hb) for detecting a significant hemorrhage (SH) in the early phase of trauma remains controversial. The present study aimed to assess the abilities of Hb measurements taken at different times throughout trauma management to identify patients with SH.
Methods: All consecutive adult trauma patients directly admitted to six French level-1 trauma centers with at least one prehospital Hb measurement were analyzed. The abilities of the following variables to identify SH (≥ 4 units of red blood cells in the first 6 h and/or death related to uncontrolled bleeding within 24 h) were determined and compared to that of shock index (SI): Hb as measured with a point-of-care (POC) device by the prehospital team on scene (POC-Hbprehosp) and upon patient's admission to the hospital (POC-Hbhosp), the difference between POC-Hbhosp and POC-Hbprehosp (DeltaPOC-Hb) and Hb as measured by the hospital laboratory on admission (Hb-Labhosp).
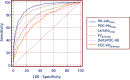
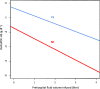
Results: A total of 6402 patients were included, 755 with SH and 5647 controls (CL). POC-Hbprehosp significantly predicted SH with an area under ROC curve (AUC) of 0.72 and best cutoff values of 12 g/dl for women and 13 g/dl for men. POC-Hbprehosp < 12 g/dl had 90% specificity to predict of SH. POC-Hbhosp and Hb-Labhosp (AUCs of 0.92 and 0.89, respectively) predicted SH better than SI (AUC = 0.77, p < 0.001); best cutoff values of POC-Hbhosp were 10 g/dl for women and 12 g/dl for men. DeltaPOC-Hb also predicted SH with an AUC of 0.77, a best cutoff value of - 2 g/dl irrespective of the gender. For a same prehospital fluid volume infused, DeltaPOC-Hb was significantly larger in patients with significant hemorrhage than in controls.
Conclusions: Challenging the classical idea that early Hb measurement is not meaningful in predicting SH, POC-Hbprehosp was able, albeit modestly, to predict significant hemorrhage. POC-Hbhosp had a greater ability to predict SH when compared to shock index. For a given prehospital fluid volume infused, the magnitude of the Hb drop was significantly higher in patients with significant hemorrhage than in controls.
Keywords: Hemoglobin; Hemorrhage; Point-of-care systems; Resuscitation; Trauma.
Figures

References
-
- EN_WHS09_Table 2.pdf [Internet]. http://www.who.int/whosis/whostat/EN_WHS09_Table2.pdf.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

