A Decision-Support Tool for Renal Mass Classification
- PMID: 29980960
- PMCID: PMC6261185
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-018-0100-0
A Decision-Support Tool for Renal Mass Classification
Abstract
We investigate the viability of statistical relational machine learning algorithms for the task of identifying malignancy of renal masses using radiomics-based imaging features. Features characterizing the texture, signal intensity, and other relevant metrics of the renal mass were extracted from multiphase contrast-enhanced computed tomography images. The recently developed formalism of relational functional gradient boosting (RFGB) was used to learn human-interpretable models for classification. Experimental results demonstrate that RFGB outperforms many standard machine learning approaches as well as the current diagnostic gold standard of visual qualification by radiologists.
Keywords: Clinical decision support; Multiphase CT; Radiomics; Renal mass; Statistical relational learning.
Figures
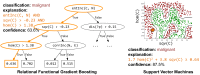

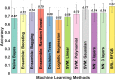
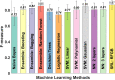
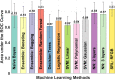
References
-
- National Cancer Institute. Cancer prevalence and cost of care projections. https:// costprojections.cancer.gov/graph.php, 2018. [Online; accessed 03-January-2018].
-
- Adam C. Mues and Jaime Landman: Small renal masses: current concepts regarding the natural history and reflections on the American Urological Association guidelines. Curr Opin Urol 20, 2010. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

