The Importance of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase as a Sensor of Unligated Okazaki Fragments during DNA Replication
- PMID: 29983321
- PMCID: PMC6060609
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.004
The Importance of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase as a Sensor of Unligated Okazaki Fragments during DNA Replication
Abstract
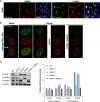
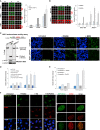
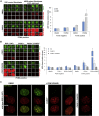
Poly(ADP-ribose) is synthesized by PARP enzymes during the repair of stochastic DNA breaks. Surprisingly, however, we show that most if not all endogenous poly(ADP-ribose) is detected in normal S phase cells at sites of DNA replication. This S phase poly(ADP-ribose) does not result from damaged or misincorporated nucleotides or from DNA replication stress. Rather, perturbation of the DNA replication proteins LIG1 or FEN1 increases S phase poly(ADP-ribose) more than 10-fold, implicating unligated Okazaki fragments as the source of S phase PARP activity. Indeed, S phase PARP activity is ablated by suppressing Okazaki fragment formation with emetine, a DNA replication inhibitor that selectively inhibits lagging strand synthesis. Importantly, PARP activation during DNA replication recruits the single-strand break repair protein XRCC1, and human cells lacking PARP activity and/or XRCC1 are hypersensitive to FEN1 perturbation. Collectively, our data indicate that PARP1 is a sensor of unligated Okazaki fragments during DNA replication and facilitates their repair.
Keywords: DNA repair; DNA replication; DNA strand break; PARP1; postreplication repair.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Mechanism for Synthetic Lethality in BRCA-Deficient Cancers: No Longer Lagging Behind.Mol Cell. 2018 Sep 20;71(6):877-878. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.08.045. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 30241603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akbari M., Peña-Diaz J., Andersen S., Liabakk N.-B., Otterlei M., Krokan H.E. Extracts of proliferating and non-proliferating human cells display different base excision pathways and repair fidelity. DNA Repair (Amst.) 2009;8:834–843. - PubMed
-
- Aladjem M.I., Wahl G.M. Mapping replication fork direction by leading strand analysis. Methods. 1997;13:281–292. - PubMed
-
- Aladjem M.I., Rodewald L.W., Kolman J.L., Wahl G.M. Genetic dissection of a mammalian replicator in the human beta-globin locus. Science. 1998;281:1005–1009. - PubMed
-
- Amé J.C., Rolli V., Schreiber V., Niedergang C., Apiou F., Decker P., Muller S., Höger T., Ménissier-de Murcia J., de Murcia G. PARP-2, A novel mammalian DNA damage-dependent poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:17860–17868. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

