Remarkable impact of steam temperature on ginsenosides transformation from fresh ginseng to red ginseng
- PMID: 29983609
- PMCID: PMC6026370
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2017.02.003
Remarkable impact of steam temperature on ginsenosides transformation from fresh ginseng to red ginseng
Abstract
Background: Temperature is an essential condition in red ginseng processing. The pharmacological activities of red ginseng under different steam temperatures are significantly different.
Methods: In this study, an ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry was developed to distinguish the red ginseng products that were steamed at high and low temperatures. Multivariate statistical analyses such as principal component analysis and supervised orthogonal partial least squared discrimination analysis were used to determine the influential components of the different samples.
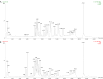
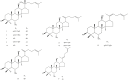
Results: The results showed that different steamed red ginseng samples can be identified, and the characteristic components were 20-gluco-ginsenoside Rf, ginsenoside Re, ginsenoside Rg1, and malonyl-ginsenoside Rb1 in red ginseng steamed at low temperature. Meanwhile, the characteristic components in red ginseng steamed at high temperature were 20R-ginsenoside Rs3 and ginsenoside Rs4. Polar ginsenosides were abundant in red ginseng steamed at low temperature, whereas higher levels of less polar ginsenosides were detected in red ginseng steamed at high temperature.
Conclusion: This study makes the first time that differences between red ginseng steamed under different temperatures and their ginsenosides transformation have been observed systematically at the chemistry level. The results suggested that the identified chemical markers can be used to illustrate the transformation of ginsenosides in red ginseng processing.
Keywords: MVA; UPLC–QTOF-MS/MS; red ginseng; steaming temperature; transformation.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Intraconversion of Polar Ginsenosides, Their Transformation into Less-Polar Ginsenosides, and Ginsenoside Acetylation in Ginseng Flowers upon Baking and Steaming.Molecules. 2018 Mar 26;23(4):759. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040759. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29587462 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Comparison of Two Drying Methods of Mountain Cultivated Ginseng by UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS and Multivariate Statistical Analysis.Molecules. 2017 Apr 30;22(5):717. doi: 10.3390/molecules22050717. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28468295 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of mountain-cultivated ginseng and cultivated ginseng using UPLC/oa-TOF MSE with a multivariate statistical sample-profiling strategy.J Ginseng Res. 2016 Oct;40(4):344-350. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2015.11.001. Epub 2015 Nov 27. J Ginseng Res. 2016. PMID: 27746686 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study on chemical composition of total saponins extracted from fermented and white ginseng under the effect of macrophage phagocytotic function.J Ginseng Res. 2017 Jul;41(3):379-385. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2017.03.009. Epub 2017 Mar 31. J Ginseng Res. 2017. PMID: 28701881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Saponins of ginseng products: a review of their transformation in processing.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 28;14:1177819. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1177819. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37188270 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Greater Efficacy of Black Ginseng (CJ EnerG) over Red Ginseng against Lethal Influenza A Virus Infection.Nutrients. 2019 Aug 13;11(8):1879. doi: 10.3390/nu11081879. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31412594 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-melanogenic property of ginsenoside Rf from Panax ginseng via inhibition of CREB/MITF pathway in melanocytes and ex vivo human skin.J Ginseng Res. 2021 Sep;45(5):555-564. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2020.11.003. Epub 2020 Dec 9. J Ginseng Res. 2021. PMID: 34803425 Free PMC article.
-
Structural-Activity Relationship of Rare Ginsenosides from Red Ginseng in the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 11;24(10):8625. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108625. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239965 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Bioactive Saponin Content of Raphanus sativus Extract by Thermal Processing at Various Conditions.Molecules. 2022 Nov 22;27(23):8125. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238125. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500218 Free PMC article.
-
Remarkable impact of commercial sterilizing on ginsenosides transformation in fresh ginseng pulp based on widely targeted metabolomics analysis.Food Chem X. 2022 Aug 9;15:100415. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2022.100415. eCollection 2022 Oct 30. Food Chem X. 2022. PMID: 36211783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kennedy D.O., Scholey A.B. Ginseng: potential for the enhancement of cognitive performance and mood. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2003;75:687–700. - PubMed
-
- Coleman C.I., Hebert J.H., Reddy P. The effects of Panax ginseng on quality of life. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2003;28:5–15. - PubMed
-
- Jiao L., Zhang X., Wang M., Li B., Liu Z., Liu S. Chemical and antihyperglycemic activity changes of ginseng pectin induced by heat processing. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;114:567–573. - PubMed
-
- Yang W.Z., Ye M., Qiao X., Liu C.F., Miao W.J., Bo T., Tao H.Y., Guo D.A. A strategy for efficient discovery of new natural compounds by integrating orthogonal column chromatography and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry analysis: its application in Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolium and Panax notoginseng to characterize 437 potential new ginsenosides. Anal Chim Acta. 2012;739:56–66. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y., Chen Y., Xu H., Luo H., Jiang R. Analgesic effects of glycoproteins from Panax ginseng root in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;148:946–950. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

