Role of IL-32 Gamma on Bone Metabolism in Autoimmune Arthritis
- PMID: 29984038
- PMCID: PMC6026691
- DOI: 10.4110/in.2018.18.e20
Role of IL-32 Gamma on Bone Metabolism in Autoimmune Arthritis
Abstract
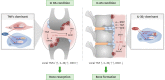
IL-32 acts as a pro-inflammatory cytokine by inducing the synthesis of inflammatory molecules as well as promoting the morphological changes involved in the transformation of monocytes into osteoclasts (OCs). Evaluation of the functions of IL-32 has mainly focused on its inflammatory properties, such as involvement in the pathogenesis of various autoimmune diseases. Recently, IL-32 was shown to be involved in bone metabolism, in which it promotes the differentiation and activation of OCs and plays a key role in bone resorption in inflammatory conditions. IL-32γ also regulates bone formation in conditions such as ankylosing spondylitis and osteoporosis. In this review, we summarize the results of recent studies on the role of IL-32γ in bone metabolism in inflammatory arthritis.
Keywords: Ankylosing spondylitis; IL-32; Inflammation; Osteoblasts; Osteoclasts; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lories R. The balance of tissue repair and remodeling in chronic arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7:700–707. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

