Weighting function effects in a direct regularization method for image-guided near-infrared spectral tomography of breast cancer
- PMID: 29984097
- PMCID: PMC6033579
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.9.003266
Weighting function effects in a direct regularization method for image-guided near-infrared spectral tomography of breast cancer
Abstract
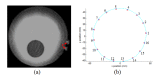
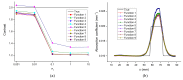
Structural image-guided near-infrared spectral tomography (NIRST) has been developed as a way to use diffuse NIR spectroscopy within the context of image-guided quantification of tissue spectral features. A direct regularization imaging (DRI) method for NIRST has the value of not requiring any image segmentation. Here, we present a comprehensive investigational study to analyze the impact of the weighting function implied when weighting the recovery of optical coefficients in DRI based NIRST. This was done using simulations, phantom and clinical patient exam data. Simulations where the true object is known indicate that changes to this weighting function can vary the contrast by 10%, the contrast to noise ratio by 20% and the full width half maximum (FWHM) by 30%. The results from phantoms and human images show that a linear inverse distance weighting function appears optimal, and that incorporation of this function can generally improve the recovered total hemoglobin contrast of the tumor to the normal surrounding tissue by more than 15% in human cases.
Keywords: (100.3010) Image reconstruction techniques; (170.3880) Medical and biological imaging; (170.6960) Tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this article.
Figures









References
-
- Lim E. A., Gunther J. E., Kim H. K., Flexman M., Hibshoosh H., Crew K., Taback B., Campbell J., Kalinsky K., Hielscher A., Hershman D. L., “Diffuse optical tomography changes correlate with residual cancer burden after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients,” Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 162(3), 533–540 (2017). 10.1007/s10549-017-4150-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
