Role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma, pathogenesis, and clinical significance
- PMID: 29984212
- PMCID: PMC6027703
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S156701
Role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma, pathogenesis, and clinical significance
Abstract
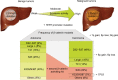
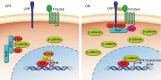
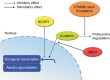
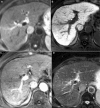
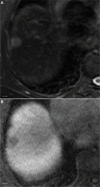
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common primary hepatic malignancies and one of the fastest-growing causes of cancer-related mortality in the United States. The molecular basis of HCC carcinogenesis has not been clearly identified. Among the molecular signaling pathways implicated in the pathogenesis of HCC, the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is one of the most frequently activated. A great effort is under way to clearly understand the role of this pathway in the pathogenesis of HCC and its role in the transition from chronic liver diseases, including viral hepatitis, to hepatocellular adenomas (HCAs) and HCCs and its targetability in novel therapies. In this article, we review the role of the β-catenin pathway in hepatocarcinogenesis and progression from chronic inflammation to HCC, the novel potential treatments targeting the pathway and its prognostic role in HCC patients, as well as the imaging features of HCC and their association with aberrant activation of the pathway.
Keywords: Wnt/β-catenin; gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging; hepatocellular carcinoma; molecular therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Shanbhogue AK, Prasad SR, Takahashi N, Vikram R, Sahani DV. Recent advances in cytogenetics and molecular biology of adult hepatocel-lular tumors: implications for imaging and management. Radiology. 2011;258(3):673–693. - PubMed
-
- Dahmani R, Just P-A, Perret C. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway as a therapeutic target in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2011;35(11):709–713. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

