CaMK4 compromises podocyte function in autoimmune and nonautoimmune kidney disease
- PMID: 29985166
- PMCID: PMC6063476
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI99507
CaMK4 compromises podocyte function in autoimmune and nonautoimmune kidney disease
Abstract
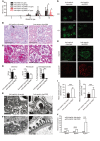
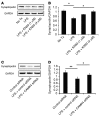
Podocyte malfunction occurs in autoimmune and nonautoimmune kidney disease. Calcium signaling is essential for podocyte injury, but the role of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase (CaMK) signaling in podocytes has not been fully explored. We report that podocytes from patients with lupus nephritis and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and lupus-prone and lipopolysaccharide- or adriamycin-treated mice display increased expression of CaMK IV (CaMK4), but not CaMK2. Mechanistically, CaMK4 modulated podocyte motility by altering the expression of the GTPases Rac1 and RhoA and suppressed the expression of nephrin, synaptopodin, and actin fibers in podocytes. In addition, it phosphorylated the scaffold protein 14-3-3β, which resulted in the release and degradation of synaptopodin. Targeted delivery of a CaMK4 inhibitor to podocytes preserved their ultrastructure, averted immune complex deposition and crescent formation, and suppressed proteinuria in lupus-prone mice and proteinuria in mice exposed to lipopolysaccharide-induced podocyte injury by preserving nephrin/synaptopodin expression. In animals exposed to adriamycin, podocyte-specific delivery of a CaMK4 inhibitor prevented and reversed podocyte injury and renal disease. We conclude that CaMK4 is pivotal in immune and nonimmune podocyte injury and that its targeted cell-specific inhibition preserves podocyte structure and function and should have therapeutic value in lupus nephritis and podocytopathies, including focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; Calcium signaling; Calmodulin; Lupus; Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Comment in
-
Pivotal role of CaMK4 in podocyte injury.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018 Oct;14(10):598. doi: 10.1038/s41581-018-0042-2. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29995833 No abstract available.
References
-
- Welsh GI, Saleem MA. The podocyte cytoskeleton--key to a functioning glomerulus in health and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011;8(1):14–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

