Simple and Effective Administration and Visualization of Microparticles in the Circulatory System of Small Fishes Using Kidney Injection
- PMID: 29985336
- PMCID: PMC6101761
- DOI: 10.3791/57491
Simple and Effective Administration and Visualization of Microparticles in the Circulatory System of Small Fishes Using Kidney Injection
Abstract
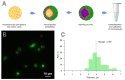
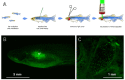
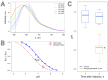
The systemic administration of micro-size particles into a living organism can be applied for vasculature visualization, drug and vaccine delivery, implantation of transgenic cells and tiny optical sensors. However, intravenous microinjections into small animals, which are mostly used in biological and veterinary laboratories, are very difficult and require trained personnel. Herein, we demonstrate a robust and efficient method for the introduction of microparticles into the circulatory system of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) by injection into the fish kidney. To visualize the introduced microparticles in the vasculature, we propose a simple intravital imaging technique in fish gills. In vivo monitoring of the zebrafish blood pH was accomplished using an injected microencapsulated fluorescent probe, SNARF-1, to demonstrate one of the possible applications of the described technique. This article provides a detailed description of the encapsulation of pH-sensitive dye and demonstrates the principles of the quick injection and visualization of the obtained microcapsules for in vivo recording of the fluorescent signal. The proposed method of injection is characterized by a low mortality rate (0-20%) and high efficiency (70-90% success), and it is easy to institute using commonly available equipment. All described procedures can be performed on other small fish species, such as guppies and medaka.
References
-
- Rivas-Aravena A, Sandino AM, Spencer E. Nanoparticles and microparticles of polymers and polysaccharides to administer fish vaccines. Biol. Res. 2013;46(4):407–419. - PubMed
-
- Yashchenok AM, Jose J, Trochet P, Sukhorukov GB, Gorin DA. Multifunctional polyelectrolyte microcapsules as a contrast agent for photoacoustic imaging in blood. J. Biophotonics. 2016;9(8):792–799. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources