Improving Postdischarge Outcomes in Acute Heart Failure
- PMID: 29985826
- PMCID: PMC6114135
- DOI: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000791
Improving Postdischarge Outcomes in Acute Heart Failure
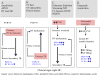
Figures


References
-
- Ambrosy AP, Fonarow GC, Butler J, et al. The global health and economic burden of hospitalizations for heart failure: lessons learned from hospitalized heart failure registries. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63(12):1123–33. - PubMed
-
- Harjola VP, Follath F, Nieminen MS, et al. Characteristics, outcomes, and predictors of mortality at 3 months and 1 year in patients hospitalized for acute heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail. 2010;12(3):239–48. - PubMed
-
- Maggioni AP, Dahlstrom U, Filippatos G, et al. EURObservational Research Programme: regional differences and 1-year follow-up results of the Heart Failure Pilot Survey (ESC-HF Pilot) Eur J Heart Fail. 2013;15(7):808–17. - PubMed
-
- Tavazzi L, Senni M, Metra M, et al. Multicenter prospective observational study on acute and chronic heart failure: one-year follow-up results of IN-HF (Italian Network on Heart Failure) outcome registry. Circ Heart Fail. 2013;6(3):473–81. - PubMed
-
- Chioncel O, Mebazaa A, Harjola VP, et al. Clinical phenotypes and outcome of patients hospitalized for acute heart failure: the ESC Heart Failure Long-Term Registry. Eur J Heart Fail. 2017;19(10):1242–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
