BCL11B mutations in patients affected by a neurodevelopmental disorder with reduced type 2 innate lymphoid cells
- PMID: 29985992
- PMCID: PMC6061686
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awy173
BCL11B mutations in patients affected by a neurodevelopmental disorder with reduced type 2 innate lymphoid cells
Abstract
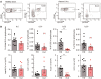
The transcription factor BCL11B is essential for development of the nervous and the immune system, and Bcl11b deficiency results in structural brain defects, reduced learning capacity, and impaired immune cell development in mice. However, the precise role of BCL11B in humans is largely unexplored, except for a single patient with a BCL11B missense mutation, affected by multisystem anomalies and profound immune deficiency. Using massively parallel sequencing we identified 13 patients bearing heterozygous germline alterations in BCL11B. Notably, all of them are affected by global developmental delay with speech impairment and intellectual disability; however, none displayed overt clinical signs of immune deficiency. Six frameshift mutations, two nonsense mutations, one missense mutation, and two chromosomal rearrangements resulting in diminished BCL11B expression, arose de novo. A further frameshift mutation was transmitted from a similarly affected mother. Interestingly, the most severely affected patient harbours a missense mutation within a zinc-finger domain of BCL11B, probably affecting the DNA-binding structural interface, similar to the recently published patient. Furthermore, the most C-terminally located premature termination codon mutation fails to rescue the progenitor cell proliferation defect in hippocampal slice cultures from Bcl11b-deficient mice. Concerning the role of BCL11B in the immune system, extensive immune phenotyping of our patients revealed alterations in the T cell compartment and lack of peripheral type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s), consistent with the findings described in Bcl11b-deficient mice. Unsupervised analysis of 102 T lymphocyte subpopulations showed that the patients clearly cluster apart from healthy children, further supporting the common aetiology of the disorder. Taken together, we show here that mutations leading either to BCL11B haploinsufficiency or to a truncated BCL11B protein clinically cause a non-syndromic neurodevelopmental delay. In addition, we suggest that missense mutations affecting specific sites within zinc-finger domains might result in distinct and more severe clinical outcomes.
Figures




References
-
- Arlotta P, Molyneaux BJ, Chen J, Inoue J, Kominami R, Macklis JD. Neuronal subtype-specific genes that control corticospinal motor neuron development in vivo. Neuron 2005; 45: 207–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

