Is a Reported Penicillin Allergy Sufficient Grounds to Forgo the Multidimensional Antimicrobial Benefits of β-Lactam Antibiotics?
- PMID: 29986019
- PMCID: PMC6293005
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciy557
Is a Reported Penicillin Allergy Sufficient Grounds to Forgo the Multidimensional Antimicrobial Benefits of β-Lactam Antibiotics?
Abstract
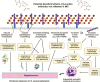
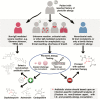
The majority of patients with reported penicillin allergy are not allergic when tested or challenged. Penicillin allergy testing has been shown to significantly reduce annual healthcare expenditures. Data have emerged showing β-lactams have multidimensional antibacterial effects in vivo, far beyond what is appreciated in standard bacteriological susceptibility testing media. These include enhancing bacterial killing by the innate immune system. Supporting the clinical relevance of these secondary underappreciated effects are recent clinical and pharmacoeconomic analyses that show worse outcomes in patients with reported penicillin allergies who receive non-β-lactam antibiotics when compared to their non-penicillin-allergic counterparts. This is particularly relevant in the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. This article reviews the tremendous advantages offered by β-lactam therapy and makes a strong case that the debunking of false penicillin allergies through a detailed allergy history and penicillin allergy testing should be a vital component of antimicrobial stewardship practices.
Figures
References
-
- Macy E. The clinical evaluation of penicillin allergy: what is necessary, sufficient and safe given the materials currently available?Clin Exp Allergy 2011; 41:1498–501. - PubMed
-
- Solensky R. Hypersensitivity reactions to beta-lactam antibiotics. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2003; 24:201–20. - PubMed
-
- Joint Task Force on Practice Parameters; American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology; American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology; Joint Council of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. Drug allergy: an updated practice parameter. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2010; 105:259–73. - PubMed
-
- Macy E, Ngor EW. Safely diagnosing clinically significant penicillin allergy using only penicilloyl-poly-lysine, penicillin, and oral amoxicillin. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2013; 1:258–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

