Fluid Management in Sepsis
- PMID: 29986619
- PMCID: PMC6532631
- DOI: 10.1177/0885066618784861
Fluid Management in Sepsis
Abstract
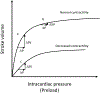
Among critically ill adults, sepsis remains both common and lethal. In addition to antibiotics and source control, fluid resuscitation is a fundamental sepsis therapy. The physiology of fluid resuscitation for sepsis, however, is complex. A landmark trial found early goal-directed sepsis resuscitation reduced mortality, but 3 recent multicenter trials did not confirm this benefit. Multiple trials in resource-limited settings have found increased mortality with early fluid bolus administration in sepsis, and the optimal approach to early sepsis resuscitation across settings remains unknown. After initial resuscitation, excessive fluid administration may contribute to edema and organ dysfunction. Using dynamic variables such as passive leg raise testing can predict a patient's hemodynamic response to fluid administration better than static variables such as central venous pressure. Whether using measures of "fluid responsiveness" to guide fluid administration improves patient outcomes, however, remains unknown. New evidence suggests improved patient outcomes with the use of balanced crystalloids compared to saline in sepsis. Albumin may be beneficial in septic shock, but other colloids such as starches, dextrans, and gelatins appear to increase the risk of death and acute kidney injury. For the clinician caring for patients with sepsis today, the initial administration of 20 mL/kg of intravenous balanced crystalloid, followed by consideration of the risks and benefits of subsequent fluid administration represents a reasonable approach. Additional research is urgently needed to define the optimal dose, rate, and composition of intravenous fluid during the management of patients with sepsis and septic shock.
Keywords: fluid therapy; intensive care unit; sepsis; shock.
Figures


References
-
- Angus DC, van der Poll T. Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock. N Engl J Med 2013;369(9):840–51. - PubMed
-
- The PRISM Investigators. Early, Goal-Directed Therapy for Septic Shock — A Patient-Level Meta-Analysis. N Engl J Med 2017;376(23):2223–34. - PubMed
-
- Monge García MI, Guijo González P, Gracia Romero M, et al. Effects of fluid administration on arterial load in septic shock patients. Intensive Care Med 2015;41(7):1247–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

