Differential composition of DHA and very-long-chain PUFAs in rod and cone photoreceptors
- PMID: 29986998
- PMCID: PMC6121944
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M082495
Differential composition of DHA and very-long-chain PUFAs in rod and cone photoreceptors
Abstract
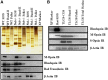
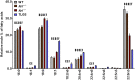
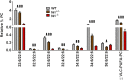
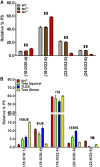
Long-chain PUFAs (LC-PUFAs; C20-C22; e.g., DHA and arachidonic acid) are highly enriched in vertebrate retina, where they are elongated to very-long-chain PUFAs (VLC-PUFAs; C 28) by the elongation of very-long-chain fatty acids-4 (ELOVL4) enzyme. These fatty acids play essential roles in modulating neuronal function and health. The relevance of different lipid requirements in rods and cones to disease processes, such as age-related macular degeneration, however, remains unclear. To better understand the role of LC-PUFAs and VLC-PUFAs in the retina, we investigated the lipid compositions of whole retinas or photoreceptor outer segment (OS) membranes in rodents with rod- or cone-dominant retinas. We analyzed fatty acid methyl esters and the molecular species of glycerophospholipids (phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphatidylserine) by GC-MS/GC-flame ionization detection and ESI-MS/MS, respectively. We found that whole retinas and OS membranes in rod-dominant animals compared with cone-dominant animals had higher amounts of LC-PUFAs and VLC-PUFAs. Compared with those of rod-dominant animals, retinas and OS membranes from cone-dominant animals also had about 2-fold lower levels of di-DHA (22:6/22:6) molecular species of glycerophospholipids. Because PUFAs are necessary for optimal G protein-coupled receptor signaling in rods, these findings suggest that cones may not have the same lipid requirements as rods.
Keywords: docosahexaenoic acid; glycerophospholipids; macular degeneration; polyunsaturated fatty acids; rod- and cone-dominant retinas; supraenoic lipids.
Figures



References
-
- Fliesler S. J., and Anderson R. E.. 1983. Chemistry and metabolism of lipids in the vertebrate retina. Prog. Lipid Res. 22: 79–131. - PubMed
-
- SanGiovanni J. P., and Chew E. Y.. 2005. The role of omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in health and disease of the retina. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 24: 87–138. - PubMed
-
- Anderson R. E., Benolken R. M., Kelleher P. A., Maude M. B., and Wiegand R. D.. 1978. Chemistry of photoreceptor membrane preparations from squid retinas. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 510: 316–326. - PubMed
-
- Benolken R. M., Anderson R. E., and Maude M. B.. 1975. Lipid composition of Limulus photoreceptor membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 413: 234–242. - PubMed
-
- Benolken R. M., Anderson R. E., and Wheeler T. G.. 1973. Membrane fatty acids associated with the electrical response in visual excitation. Science. 182: 1253–1254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

