Interleukin-33: Its Emerging Role in Allergic Diseases
- PMID: 29987222
- PMCID: PMC6099536
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23071665
Interleukin-33: Its Emerging Role in Allergic Diseases
Abstract
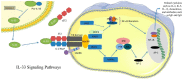
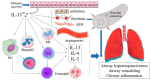
Allergic diseases, which include asthma, allergic rhinitis (AR), chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), atopic dermatitis (AD), food allergy (FA), allergic keratoconjunctivitis, seriously affect the quality of life of people all over the world. Recently, interleukin-33 (IL-33) has been found to play an important role in these refractory disorders, mainly by inducing T helper (Th) 2 immune responses. This article reviews the mobilization and biological function of IL-33 in allergic disorders, providing novel insights for addressing these hypersensitive conditions.
Keywords: Th2-type immunity; allergic diseases; asthma; interleukin-33; target therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Schmitz J., Owyang A., Oldham E., Song Y., Murphy E., McClanahan T.K., Zurawski G., Moshrefi M., Qin J., Li X., et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity. 2005;23:479–490. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.09.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pichery M., Mirey E., Mercier P., Lefrancais E., Dujardin A., Ortega N., Girard J.P. Endogenous IL-33 is highly expressed in mouse epithelial barrier tissues, lymphoid organs, brain, embryos, and inflamed tissues: In situ analysis using a novel Il-33-LacZ gene trap reporter strain. J. Immunol. 2012;188:3488–3495. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101977. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

