Quercetin Treatment Improves Renal Function and Protects the Kidney in a Rat Model of Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 29987270
- PMCID: PMC6069490
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.909259
Quercetin Treatment Improves Renal Function and Protects the Kidney in a Rat Model of Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
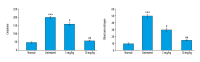
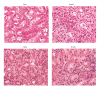
BACKGROUND The aim of this study was to examine the effects of the natural flavonoid, quercetin, in a rat model of adenine-induced chronic kidney disease. MATERIAL AND METHODS Forty male Wister rats were divided into four groups: normal (no adenine or quercetin) (n=10); untreated model (treated withadenine but not quercetin) (n=10); quercetin-treated model (5 mg/kg/day for 21 days) (n=10); quercetin-treated model (10 mg/kg/day for 21 days) (n=10). Urine and blood samples were collected and rat kidneys were examined histologically. RESULTS Comparison of the findings of the model rats treated with quercetin (n=20) with non-treated model rats (n=10) showed reduced levels of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23): normal group, 19.6 pg/ml; untreated group, 73.6 pg/ml; quercetin-treated group (5 mg/kg), 34.25 pg/ml; and quercetin-treated group (10 mg/kg), 21.3 pg/ml. Quercetin-treated model rats had reduced serum levels of parathyroid hormone (PTH), inorganic phosphate, increased urine protein-to-creatinine ratio, increased urine antioxidants, serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and interleukin (IL)-8 when compared with the untreated model group and the control group. Quercetin treatment 10 mg/kg (n=10) reduced the levels of creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and urinary uric acid. Renal histopathology in model rats treated with quercetin (n=20) showed reduced inflammation compared with the untreated model rats (n=10). CONCLUSIONS In a rat model of adenine-induced chronic kidney disease, treatment with quercetin improved renal function, reduced oxidative stress factors, serum levels of FGF23, and kidney inflammation.
Figures
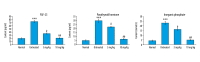
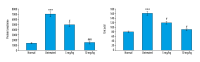

References
-
- Sarnak MJ, Astor BC. Implications of proteinuria: CKD progression and cardiovascular outcomes. Adv Chronic Kidney, Dis. 2011;18:258–66. - PubMed
-
- Faul C. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and the heart. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2012;21:369–75. - PubMed
-
- Nakano C, Hamano T, Fujii N, et al. Intact fibroblast growth factor 23 levels predict incident cardiovascular event before but not after the start of dialysis. Bone. 2012;50:1266–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

