Graphene quantum dots prevent α-synucleinopathy in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 29988049
- PMCID: PMC6351226
- DOI: 10.1038/s41565-018-0179-y
Graphene quantum dots prevent α-synucleinopathy in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
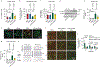
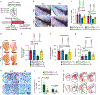
Though emerging evidence indicates that the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease is strongly correlated to the accumulation1,2 and transmission3,4 of α-synuclein (α-syn) aggregates in the midbrain, no anti-aggregation agents have been successful at treating the disease in the clinic. Here, we show that graphene quantum dots (GQDs) inhibit fibrillization of α-syn and interact directly with mature fibrils, triggering their disaggregation. Moreover, GQDs can rescue neuronal death and synaptic loss, reduce Lewy body and Lewy neurite formation, ameliorate mitochondrial dysfunctions, and prevent neuron-to-neuron transmission of α-syn pathology provoked by α-syn preformed fibrils5,6. We observe, in vivo, that GQDs penetrate the blood-brain barrier and protect against dopamine neuron loss induced by α-syn preformed fibrils, Lewy body/Lewy neurite pathology and behavioural deficits.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Untangling alpha synuclein fibrils by graphene quantum dots.Mov Disord. 2018 Nov;33(11):1673. doi: 10.1002/mds.27511. Mov Disord. 2018. PMID: 30485906 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Dawson TM & Dawson VL Molecular pathways of neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Science 302, 819–822 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Spillantini MG et al. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388, 839–840 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Li JY et al. Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in subjects with Parkinson’s disease suggest host-to-graft disease propagation. Nat. Med 14, 501–503 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

