Maintenance of CD4 T cell fitness through regulation of Foxo1
- PMID: 29988091
- PMCID: PMC6289177
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-018-0157-4
Maintenance of CD4 T cell fitness through regulation of Foxo1
Abstract
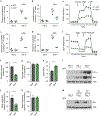
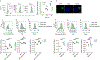
Foxo transcription factors play an essential role in regulating specialized lymphocyte functions and in maintaining T cell quiescence. Here, we used a system in which Foxo1 transcription-factor activity, which is normally terminated upon cell activation, cannot be silenced, and we show that enforcing Foxo1 activity disrupts homeostasis of CD4 conventional and regulatory T cells. Despite limiting cell metabolism, continued Foxo1 activity is associated with increased activation of the kinase Akt and a cell-intrinsic proliferative advantage; however, survival and cell division are decreased in a competitive setting or growth-factor-limiting conditions. Via control of expression of the transcription factor Myc and the IL-2 receptor β-chain, termination of Foxo1 signaling couples the increase in cellular cholesterol to biomass accumulation after activation, thereby facilitating immunological synapse formation and mTORC1 activity. These data reveal that Foxo1 regulates the integration of metabolic and mitogenic signals essential for T cell competitive fitness and the coordination of cell growth with cell division.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
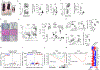

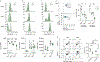
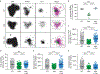
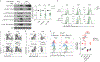
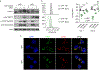
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AI126143/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI124693/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA065493/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL118979/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI051731/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI034495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL146358/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL018646/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA211015/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007529/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI101407/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI056299/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI106677/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL056067/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL056067/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA176624/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

