Schwannoma in the Supraclavicular Region: Case Report
- PMID: 29988291
- PMCID: PMC6017201
- DOI: 10.5152/tao.2018.2579
Schwannoma in the Supraclavicular Region: Case Report
Abstract
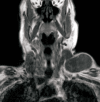
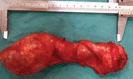
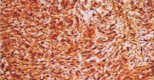
Schwannomas are benign tumors arising from schwann cells in peripheral, cranial, and autonomic nerve sheaths. Approximately half of all cases of schwannomas are observed in the head and neck region. In this study, a 71-year-old male patient presenting with a stiff mobile mass in the left supraclavicular region and diagnosed as a schwannoma after total excision was presented.
Keywords: Schwannoma; benign tumor; neck; supraclavicular region.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Erbek HS, Erbek SS, Tosun E, Çakmak Ö. Intraparotid facial nerve schwannoma: a case report. KBB ve BBC Dergisi. 2005;13:39–43.
-
- Weber AL, Montandon C, Robson CD. Neurogenic tumors of the neck. Radiol Clin North Am. 2000;38:1077–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0033-8389(05)70222-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Valentino J, Boggess MA, Ellis JL, Hester TO, Jones RO. Expected neurologic outcomes for surgical treatment of cervical neurilemmomas. Laryngoscope. 1998;108:1009–13. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-199807000-00011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bradley N, Bowerman JE. Parapharyngeal neurilemmomas. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1989;27:139–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/0266-4356(89)90061-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Capparpur C, Büyüklü F, Çakmak İ, Öztop L, Özlüoğlu LN. Schwannoma arising from cervical sympathetic chain: a case report. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2002;40:153–6.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources