IL-33/ST2 Pathway and Galectin-3 as a New Analytes in Pathogenesis and Cardiometabolic Risk Evaluation in Psychosis
- PMID: 29988422
- PMCID: PMC6024021
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00271
IL-33/ST2 Pathway and Galectin-3 as a New Analytes in Pathogenesis and Cardiometabolic Risk Evaluation in Psychosis
Abstract
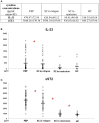
Schizophrenia and treatment of this disorder are often accompanied with metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular issues. Alterations in the serum level of innate immune mediators, such as interleukin-33 (IL-33) and its receptor IL-33R (ST2) and Galectin-3 (Gal-3) were observed in these conditions. Moreover, these parameters are potential prognostic and therapeutic markers. There is also accumulating evidence that these molecules play a role in neuroinflammation. Therefore, in this study we have investigated the serum level of Gal-3, IL-33 and soluble ST2 (sST2) in different stages of schizophrenia. Gal-3 levels were elevated in remission and lower in schizophrenia exacerbation in comparison with controls. Levels of IL-33 and sST2 are higher in schizophrenia exacerbation in comparison with controls and patients in remission. This initial analysis of new markers of neuroinflammation suggested their involvement in schizophrenia pathophysiology and/or cardiometabolic comorbidity.
Keywords: cardiovascular issues; galectin-3; interleukin-33; metabolic syndrome; schizophrenia.
Figures

References
-
- American Diabetes Association, American Psychiatric Association, American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, North American Association for the Study of Obesity Consensus development conference on antipsychotic drugs and obesity and diabetes. Diabetes Care (2004) 27:596–601. 10.2337/diacare.27.2.596 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

