Role of Hepatic Deposited Immunoglobulin G in the Pathogenesis of Liver Damage in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- PMID: 29988500
- PMCID: PMC6026631
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01457
Role of Hepatic Deposited Immunoglobulin G in the Pathogenesis of Liver Damage in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
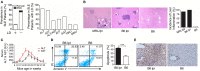
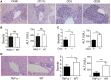
The onset of hepatic disorders in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is frequent; however, the etiology and liver pathogenesis of SLE remain unknown. In the present study, the role of hepatic deposited immunoglobulin G (IgG) in SLE-derived liver damage was investigated. From a retrospective analysis of the medical records of 404 patients with lupus and from experimental studies on mice models, we found that liver dysfunction is common in SLE and liver damage with IgG deposition spontaneously develops in lupus-prone mice. Liver injury was recreated in mice by injecting IgG from lupus serum intrahepatically. The inflammation intensity in the liver decreased with IgG depletion and the lupus IgG-induced liver inflammation in FcγRIII-deficient mice was comparatively low; while, inflammation was increased in FcγRIIb-deficient mice. Macrophages, Kupffer cells, natural killer cells, and their products, but not lymphocytes, are required for the initiation of SLE-associated liver inflammation. Blocking IgG signaling using a spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) inhibitor suppressed the liver damage. Our findings provided evidence of spontaneously established liver damage in SLE. They also suggested that hepatic-deposited lupus IgG is an important pathological factor in the development of liver injury and that hepatic inflammation is regulated by the Syk signaling pathway. Thus, Syk inhibition might promote the development of a therapeutic strategy to control liver damage in patients with SLE.
Keywords: hepatitis; immunoglobulin G deposition; innate immune cells; spleen tyrosine kinase; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The role of organ-deposited IgG in the pathogenesis of multi-organ and tissue damage in systemic lupus erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 13;13:924766. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.924766. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36311714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis of Skin Injury of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2018 Feb 21;20(2):5. doi: 10.1007/s11926-018-0713-9. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29464447 Review.
-
Predominant Role of Immunoglobulin G in the Pathogenesis of Splenomegaly in Murine Lupus.Front Immunol. 2020 Jan 24;10:3020. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03020. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32082297 Free PMC article.
-
The role of neutrophils in skin damage induced by tissue-deposited lupus IgG.Immunology. 2018 Feb 16;154(4):604-12. doi: 10.1111/imm.12908. Online ahead of print. Immunology. 2018. PMID: 29450882 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the mechanism of action of lanraplenib, a novel spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in models of lupus nephritis.BMC Rheumatol. 2021 Mar 30;5(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s41927-021-00178-3. BMC Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 33781343 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Chronic exposure to PM2.5 aggravates SLE manifestations in lupus-prone mice.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2021 Mar 25;18(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12989-021-00407-0. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33766080 Free PMC article.
-
Gefitinib and fostamatinib target EGFR and SYK to attenuate silicosis: a multi-omics study with drug exploration.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 May 13;7(1):157. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00959-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35551173 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulin G inhibits glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis through occupation of FcγRI.iScience. 2023 Aug 26;26(10):107749. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107749. eCollection 2023 Oct 20. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37701568 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of Lupus Serum-Induced Skin Inflammation in CD64-Deficient Mice.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 22;13:824008. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.824008. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35273604 Free PMC article.
-
The spleen tyrosine kinase (SYK): A crucial therapeutic target for diverse liver diseases.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 7;8(12):e12130. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12130. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36568669 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu Y, Yu J, Oaks Z, Marchena-Mendez I, Francis L, Bonilla E, et al. Liver injury correlates with biomarkers of autoimmunity and disease activity and represents an organ system involvement in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol (2015) 160(2):319–27.10.1016/j.clim.2015.07.001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

