Foramen tympanicum with symptomatic temporomandibular joint herniation
- PMID: 29988923
- PMCID: PMC6034154
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2018.05.009
Foramen tympanicum with symptomatic temporomandibular joint herniation
Abstract
Foramen tympanicum (FT), or foramen of Huschke, describes an uncommon anatomicvariant of a persistent bony defect connecting the external acoustic meatus to the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). Although rare, it can be associated with significant complications, such as TMJ herniation, salivary gland fistula, infectious or tumoral spread between the external acoustic meatus and the TMJ, or result in inadvertent ear injury during TMJ arthroscopy. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case report of a symptomatic FT with a full description of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Surgical exploration confirmed the presence of FT with TMJ herniation with subsequent successful closure of the defect obtained.
Keywords: Anatomic variation; External acoustic canal; Magnetic resonance imaging; Temporomandibular joint; X-ray computed tomography.
Figures
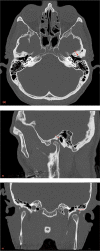
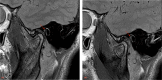
Similar articles
-
Spontaneous temporomandibular joint herniation into the external auditory canal through a persistent foramen tympanicum (Huschke): radiographic features.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2013 Jan-Feb;37(1):111-3. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0b013e318272ef04. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2013. PMID: 23321842
-
Perspective on Temporomandibular Joint Disorder: Foramen Tympanicum Defect.J Oral Rehabil. 2024 Jun;51(6):992-997. doi: 10.1111/joor.13677. Epub 2024 Mar 3. J Oral Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38433411
-
Temporomandibular Joint Herniation Into the External Auditory Canal: Two Cases Involving a Persistent Foramen Tympanicum.J Craniofac Surg. 2015 Jun;26(4):e331-3. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000001630. J Craniofac Surg. 2015. PMID: 26080253
-
Bilateral spontaneous symptomatic temporomandibular joint herniation into the external auditory canal: A case report and literature review.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2018 Apr;45(2):346-350. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2017.03.011. Epub 2017 Apr 14. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2018. PMID: 28416346 Review.
-
Persistent foramen of Huschke: Clinical manifestations and complications, systematic review.J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2023 Dec;124(6):101455. doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2023.101455. Epub 2023 Mar 24. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2023. PMID: 36965816
Cited by
-
Otoscopy and imaging features of spontaneous temporomandibular joint herniation into the external auditory canal.BJR Open. 2020 May 21;2(1):20200005. doi: 10.1259/bjro.20200005. eCollection 2020. BJR Open. 2020. PMID: 33178972 Free PMC article.
-
A Persistent Foramen of Huschke: A Small Road to Misery in Necrotizing External Otitis.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019 Sep;40(9):1552-1556. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6161. Epub 2019 Aug 8. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019. PMID: 31395661 Free PMC article.
-
Finding the Silver Bullet for Persistent Foramen Hushke.Cureus. 2024 Jan 23;16(1):e52791. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52791. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38389601 Free PMC article.
-
Determining the existence of the foramen of Huschke in patients with temporomandibular joint disorders using cone beam computed tomography: retrospective cohort study.BMC Med Imaging. 2022 Aug 13;22(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s12880-022-00850-1. BMC Med Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35963990 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hashimoto T., Ojiri H., Kawai Y. The foramen of Huschke: age and gender specific features after childhood. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;40:743–746. - PubMed
-
- Singh I., Jain A., Prasad P., Rajpurohit P. Spontaneous temporomandibular joint herniation: a rare case. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;21(1):87–90. - PubMed
-
- Rushton V.E., Pemberton M.N. Salivary otorrhoea: a case report and a review of the literature. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2005;34(6):37–379. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

