Impact of histologic subtypes and treatment modality among patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma: a SEER database analysis
- PMID: 29988979
- PMCID: PMC6034756
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.25622
Impact of histologic subtypes and treatment modality among patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma: a SEER database analysis
Abstract
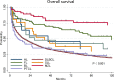
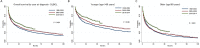
Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) is a rare and aggressive extranodal presentation of lymphoma; however, the data for outcomes of patients with subtypes other than diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) are limited. Therefore, we analyzed overall survival (OS) of adult patients diagnosed with PCNSL by histologic subtype between 1998 and 2014 using the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results. A total of 4375 patients were identified. The median age of the patients was 64 years (range: 18-96). DLBCL was the most common histology (N=3,091), followed by follicular lymphoma (FL, N=83), peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL, N=64), marginal zone lymphoma (MZL, N=63), Burkitt lymphoma (BL, N=27), small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL, N=22), Hodgkin lymphoma (HL, N=13) and others (N=1,012). The 5-year OS rates were 30% in DLBCL, 66% in FL, 33% in PTCL, 79% in MZL, 42% in BL, 38% in SLL and 45% in HL. Radiation alone showed similar OS compared to no treatment in DLBCL, BL and PTCL, while radiation alone was associated with similar OS to chemotherapy or chemo-radiation in FL and MZL. The outcomes of patients with PCNSL are unfavorable; with the exception of FL and MZL which can potentially show prolonged survival with surgical resection or radiation monotherapy.
Keywords: SEER; follicular lymphoma; marginal zone lymphoma; primary central nervous system lymphoma; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Network NCC Central Nervous System Cancers. 2017.
-
- Poortmans PM, Kluin-Nelemans HC, Haaxma-Reiche H, Van't Veer M, Hansen M, Soubeyran P, Taphoorn M, Thomas J, Van den Bent M, Fickers M, Van Imhoff G, Rozewicz C, Teodorovic I, et al. High-dose methotrexate-based chemotherapy followed by consolidating radiotherapy in non-AIDS-related primary central nervous system lymphoma: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Lymphoma Group Phase II Trial 20962. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:4483–4488. - PubMed
-
- DeAngelis LM, Seiferheld W, Schold SC, Fisher B, Schultz CJ, Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Study 93-10 Combination chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary central nervous system lymphoma: Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Study 93-10. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:4643–4648. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

