Saturated fatty acid combined with lipopolysaccharide stimulates a strong inflammatory response in hepatocytes in vivo and in vitro
- PMID: 29989851
- PMCID: PMC6293169
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00015.2018
Saturated fatty acid combined with lipopolysaccharide stimulates a strong inflammatory response in hepatocytes in vivo and in vitro
Abstract
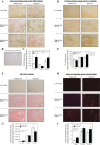
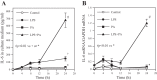
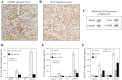
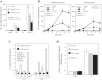
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common chronic liver disease and consumption of high-fat diet (HFD) is a risk factor for NAFLD. The HFD not only increases intake of saturated fatty acid (SFA) but also induces metabolic endotoxemia, an HFD-associated increase in circulating lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Although it is known that SFA or LPS promote hepatic inflammation, a hallmark of NAFLD, it remains unclear how SFA in combination with LPS stimulates host inflammatory response in hepatocytes. In this study, we performed both in vivo and in vitro experiments to investigate the effect of SFA in combination with LPS on proinflammatory gene expression in hepatocytes. Our animal study showed that feeding low-density lipoprotein-deficient mice HFD enriched with SFA and injection of low-dose LPS cooperatively stimulated IL-6 expression in livers. To understand how SFA and LPS interact to promote IL-6 expression, our in vitro studies showed that palmitic acid (PA), a major SFA, and LPS exerted synergistic effect on the expression of IL-6 in hepatocytes. Furthermore, coculture of hepatocytes with macrophages resulted in a greater IL-6 expression than culture of hepatocytes without macrophages in response to the combination of PA and LPS. Finally, we observed that LPS and PA increased ceramide production by cooperatively stimulating ceramide de novo synthesis, which played an essential role in the synergistic stimulation of proinflammatory gene expression by LPS and PA. Taken together, this study showed that SFA in combination with LPS stimulated a strong inflammatory response in hepatocytes in vivo and in vitro.
Keywords: ceramide; fatty acid; hepatocyte; inflammation; lipopolysaccharide.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dietary saturated fatty acid and polyunsaturated fatty acid oppositely affect hepatic NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome through regulating nuclear factor-kappa B activation.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Feb 28;22(8):2533-44. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2533. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26937141 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative stimulation of atherogenesis by lipopolysaccharide and palmitic acid-rich high fat diet in low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice.Atherosclerosis. 2017 Oct;265:231-241. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.09.008. Epub 2017 Sep 9. Atherosclerosis. 2017. PMID: 28934649 Free PMC article.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-delta agonist ameliorated inflammasome activation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Dec 7;21(45):12787-99. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i45.12787. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26668503 Free PMC article.
-
A new frontier for fat: dietary palmitic acid induces innate immune memory.Immunometabolism (Cobham). 2023 May 15;5(2):e00021. doi: 10.1097/IN9.0000000000000021. eCollection 2023 Apr. Immunometabolism (Cobham). 2023. PMID: 37197687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of dietary fat quality on metabolic endotoxaemia: a systematic review.Br J Nutr. 2020 Oct 14;124(7):654-667. doi: 10.1017/S0007114520001658. Epub 2020 May 8. Br J Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32381135
Cited by
-
Role of HO-1 against Saturated Fatty Acid-Induced Oxidative Stress in Hepatocytes.Nutrients. 2021 Mar 19;13(3):993. doi: 10.3390/nu13030993. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33808635 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and molecular effects of silymarin on the transdifferentiation processes of LX-2 cells and its connection with lipid metabolism.Mol Cell Biochem. 2020 May;468(1-2):129-142. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03717-7. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32185674
-
TLCD1 and TLCD2 regulate cellular phosphatidylethanolamine composition and promote the progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 14;13(1):6020. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33735-6. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36241646 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine inhibits free fatty acid and LPS-induced inflammation via modulating ER stress response in macrophages and hepatocytes.PLoS One. 2020 May 1;15(5):e0232630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232630. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32357187 Free PMC article.
-
Amitriptyline inhibits nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and atherosclerosis induced by high-fat diet and LPS through modulation of sphingolipid metabolism.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Feb 1;318(2):E131-E144. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00181.2019. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 31821039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beutler B. TLR4 as the mammalian endotoxin sensor. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 270: 109–120, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Brunt EM, Kleiner DE, Wilson LA, Belt P, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, NASH Clinical Research Network (CRN) . Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) activity score and the histopathologic diagnosis in NAFLD: distinct clinicopathologic meanings. Hepatology 53: 810–820, 2011. doi:10.1002/hep.24127. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

