Gonorrhoea treatment failure caused by a Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain with combined ceftriaxone and high-level azithromycin resistance, England, February 2018
- PMID: 29991383
- PMCID: PMC6152157
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2018.23.27.1800323
Gonorrhoea treatment failure caused by a Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain with combined ceftriaxone and high-level azithromycin resistance, England, February 2018
Abstract
We describe a gonorrhoea case with combined high-level azithromycin resistance and ceftriaxone resistance. In February 2018, a heterosexual male was diagnosed with gonorrhoea in the United Kingdom following sexual intercourse with a locally resident female in Thailand and failed treatment with ceftriaxone plus doxycycline and subsequently spectinomycin. Resistance arose from two mechanisms combining for the first time in a genetic background similar to a commonly circulating strain. Urgent action is essential to prevent further spread.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance; antimicrobial treatment, whole-genome sequencing; gonorrhoea; treatment failure.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
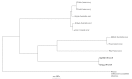
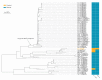
References
-
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and zone diameters. Version 8.1. Växjö: EUCAST; 2018. Available from: http://www.eucast.org.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
