UDAY: A comprehensive diabetes and hypertension prevention and management program in India
- PMID: 29991625
- PMCID: PMC6082491
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-015919
UDAY: A comprehensive diabetes and hypertension prevention and management program in India
Abstract
Introduction: Diabetes and hypertension are two leading non-communicable conditions, which are suboptimally managed in India. Thus, innovative comprehensive approaches that can concomitantly improve their detection, prevention and control are warranted.
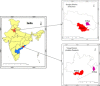
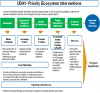
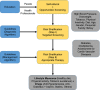
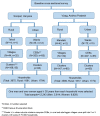
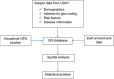
Methods and analysis: UDAY, a 5-year initiative, aims to reduce the risk of diabetes and hypertension and improve management by implementing a comprehensive intervention programme in the two selected study sites, Sonipat and Visakhapatnam (Vizag). It has a pre-post evaluation design with representative cross-sectional surveys before and after intervention. Within these two sites, urban and rural subsites each with a total population of approximately 100 000 people each were selected and a baseline and postintervention assessment was conducted deploying five surveys [among general population (including body measurements or biosamples), patients, healthcare providers including physicians and pharmacists, health facilities], which will determine the knowledge levels about diabetes and hypertension, the proportion treated and controlled; the patient knowledge and self-management skills; healthcare providers' management practices; the level of access and barriers to obtaining care.The interventions will include: tailored health promotion for improving public knowledge; screening of adults aged ≥ 30 years for identifying those at high risk of diabetes and/or hypertension for linkage to the healthcare system; patient education using technology enabled community health workers, geographic information system (GIS) based mapping of the communities, healthcare provider training on management guidelines, community based diabetes registry and; advocacy to improve access to healthcare. The baseline surveys have been completed, the study areas mapped using GIS and the interventions are being implemented. UDAY is expected to increase over baseline the levels of: public knowledge about diabetes and hypertension; those treated and controlled; patient self-management skills; the use of guideline based management by providers and; access to healthcare, leading to improved health outcomes and inform development of a India relevant chronic care model.
Ethics and dissemination: Ethical clearance for conduct of the study was obtained from the Institutional Ethics Committee (IEC) of the Public Health Foundation of India. The findings will be targeted primarily at public health policymakers and advocates, but will be disseminated widely through other mechanisms including conference presentations and peer-reviewed publications, as well as to the participating communities.
Keywords: epidemiology; general diabetes; hypertension.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Country Office for India. National multisectoral action plan for prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases. India, New Delhi: World Health Organization (WHO) Country Office for India, 2013.
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 7th edn Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation, 2015.
-
- Mohan S, Koller T. Hypertension and related comorbidities in India: Implications for the health system. India, New Delhi: World Health Organization (WHO) Country Office for India, 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical