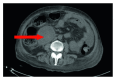
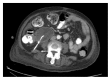
Pancreas as an Occult Source of Recurrent Salmonella enteritidis Bacteremia in an Immunocompromised Patient
- PMID: 29992065
- PMCID: PMC6016173
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/7296295
Pancreas as an Occult Source of Recurrent Salmonella enteritidis Bacteremia in an Immunocompromised Patient
Abstract
Salmonella infection usually presents as gastroenteritis and enteric fever. Some cases of bacteremia can lead to invasion of different organ systems and become occult sources for recurrence. Almost all organs of the body can be affected and have been reported in the literature. We report a rare case of repeated Salmonella enteritidis infection in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. She was treated with intravenous and oral antibiotics but still had recurrence of fevers and bacteremia. After a thorough workup, pancreatic abscesses were identified and drained with abscess culture revealing Salmonella enteritidis. She was then treated with a prolonged course of antibiotics and finally cleared the infection. This case demonstrates that nontyphoid Salmonella can be invasive and cause persistent infection. This is particularly pertinent in immunocompromised patients who are at an increased risk of infection. An aggressive workup and prolonged antibiotic course might be beneficial for this subset of patients.
Figures
References
-
- Mofredj A., Laribi K., Delcenserie R., et al. Acute pancreatitis and pancreatic reactions due to Salmonella. A study of 6 cases. Clinical and Biological Gastroenterology. 2002;26:88–92. - PubMed
-
- Rodríguez M., Diego I. D., Martínez N., Rodicio M. R., Mendoza M. C. Nontyphoidal Salmonella causing focal infections in patients admitted at a Spanish general hospital during an 11-year period (1991 to 2001) International Journal of Medical Microbiology. 2006;296(4-5):211–222. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2006.01.068. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsao C. H., Chen C. Y., Ou L. S., Huang J. L. Risk factors of mortality for Salmonella infection in systemic lupus erythematosus. Journal of Rheumatology. 2002;29(6):1214–1218. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources