The expression of MMP-1 and MMP-9 is up-regulated by smooth muscle cells after their cross-talk with macrophages in high glucose conditions
- PMID: 29992758
- PMCID: PMC6111860
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13728
The expression of MMP-1 and MMP-9 is up-regulated by smooth muscle cells after their cross-talk with macrophages in high glucose conditions
Abstract
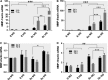
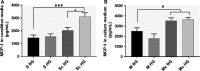
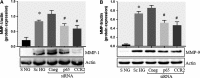
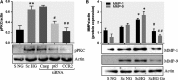
Patients with diabetes mellitus have an increased risk of myocardial infarction and coronary artery disease-related death, exhibiting highly vulnerable plaques. Many studies have highlighted the major role of macrophages (MAC) and smooth muscle cells (SMC) and the essential part of metalloproteases (MMPs) in atherosclerotic plaque vulnerability. We hypothesize that in diabetes, the interplay between MAC and SMC in high glucose conditions may modify the expression of MMPs involved in plaque vulnerability. The SMC-MAC cross-talk was achieved using trans-well chambers, where human SMC were grown at the bottom and human MAC in the upper chamber in normal (NG) or high (HG) glucose concentration. After cross-talk, the conditioned media and cells were isolated and investigated for the expression of MMPs, MCP-1 and signalling molecules. We found that upon cross-talk with MAC in HG, SMC exhibit: (i) augmented expression of MMP-1 and MMP-9; (ii) significant increase in the enzymatic activity of MMP-9; (iii) higher levels of soluble MCP-1 chemokine which is functionally active and involved in MMPs up-regulation; (iv) activated PKCα signalling pathway which, together with NF-kB are responsible for MMP-1 and MMP-9 up-regulation, and (v) impaired function of collagen assembly. Taken together, our data indicate that MCP-1 released by cell cross-talk in diabetic conditions binds to CCR2 and triggers MMP-1 and MMP-9 over-expression and activity, features that could explain the high vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaque found at diabetic patients.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; cell cross-talk; high glucose; matrix metalloproteinases; protein kinase C.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures



References
-
- Moreno V, Fuster PR. New aspects in the pathogenesis of diabetic atherothrombosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:2293‐2300. - PubMed
-
- Booth GL, Kapral MK, Fung K, Tu JV. Relation between age and cardiovascular disease in men and women with diabetes compared with non‐diabetic people: a population‐based retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2006;368:29‐36. - PubMed
-
- Varani J, Perone P, Fligiel SEG, Fisher GJ, Voorhees JV. Inhibition of type I procollagen production in photodamage: correlation between presence of highmolecular weight collagen fragments and reduced procollagen synthesis. J Investig Dermatol. 2002;119:122‐129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

