Discovery of a drug candidate for GLIS3-associated diabetes
- PMID: 29992946
- PMCID: PMC6041295
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04918-x
Discovery of a drug candidate for GLIS3-associated diabetes
Abstract
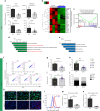
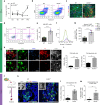
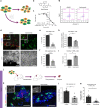
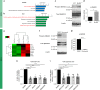
GLIS3 mutations are associated with type 1, type 2, and neonatal diabetes, reflecting a key function for this gene in pancreatic β-cell biology. Previous attempts to recapitulate disease-relevant phenotypes in GLIS3-/- β-like cells have been unsuccessful. Here, we develop a "minimal component" protocol to generate late-stage pancreatic progenitors (PP2) that differentiate to mono-hormonal glucose-responding β-like (PP2-β) cells. Using this differentiation platform, we discover that GLIS3-/- hESCs show impaired differentiation, with significant death of PP2 and PP2-β cells, without impacting the total endocrine pool. Furthermore, we perform a high-content chemical screen and identify a drug candidate that rescues mutant GLIS3-associated β-cell death both in vitro and in vivo. Finally, we discovered that loss of GLIS3 causes β-cell death, by activating the TGFβ pathway. This study establishes an optimized directed differentiation protocol for modeling human β-cell disease and identifies a drug candidate for treating a broad range of GLIS3-associated diabetic patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have filed a patent of the differentiation strategy. The authors declare no other competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK096239/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DP3 DK111907-01/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

