Angiotensin receptor and tumor necrosis factor-α activation contributes to glucose intolerance independent of systolic blood pressure in obese rats
- PMID: 29993275
- PMCID: PMC6230730
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00156.2018
Angiotensin receptor and tumor necrosis factor-α activation contributes to glucose intolerance independent of systolic blood pressure in obese rats
Abstract
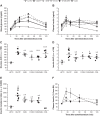
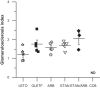
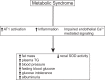
Pathological activation of the renin-angiotensin system and inflammation are associated with hypertension and the development of metabolic syndrome (MetS). The contributions of angiotensin receptor type 1 (AT1) activation, independent of blood pressure, and inflammation to glucose intolerance and renal damage are not well defined. Using a rat model of MetS, we hypothesized that the onset of glucose intolerance is primarily mediated by AT1 activation and inflammation independent of elevated systolic blood pressure (SBP). To address this hypothesis, we measured changes in SBP, adiposity, plasma glucose and triglyceride levels, and glucose tolerance in six groups of rats: 1) lean, strain control Long-Evans Tokushima Otsuka (LETO; n = 5), 2) obese Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF; n = 8), 3) OLETF + angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB; 10 mg olmesartan/kg; n = 8), 4) OLETF + tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) inhibitor (ETAN; 1.25 mg etanercept/kg; n = 6), 5) OLETF + TNF-α inhibitor + angiotensin receptor blocker (ETAN+ARB; 1.25 mg etanercept/kg + 10 mg olmesartan/kg; n = 6), and 6) OLETF + calcium channel blocker (CCB; 5 mg amlodipine/kg; n = 7). ARB and ETAN+ARB were most effective at decreasing SBP in OLETF, and ETAN did not offer any additional reduction. Glucose tolerance improved in ARB, ETAN, and ETAN+ARB compared with OLETF, whereas CCB had no detectable effect. Furthermore, all treatments reduced adiposity, whereas ETAN alone normalized urinary albumin excretion. These results suggest that AT1 activation and inflammation are primary factors in the development of glucose intolerance in a setting of MetS and that the associated increase in SBP is primarily mediated by AT1 activation.
Keywords: hypertension; inflammation; insulin resistance; metabolic syndrome; renin-angiotensin system.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Chronic AT1 blockade improves hyperglycemia by decreasing adipocyte inflammation and decreasing hepatic PCK1 and G6PC1 expression in obese rats.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Nov 1;321(5):E714-E727. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00584.2020. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34658252 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin receptor blockade increases pancreatic insulin secretion and decreases glucose intolerance during glucose supplementation in a model of metabolic syndrome.Endocrinology. 2012 Apr;153(4):1684-95. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-1885. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22355070 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic AT1 blockade improves glucose homeostasis in obese OLETF rats.J Endocrinol. 2018 Jun;237(3):271-284. doi: 10.1530/JOE-17-0678. Epub 2018 Apr 11. J Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29643115 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis of the effect of angiotensin receptor blockers and calcium channel blockers on blood pressure, glycemia and the HOMA-IR index in non-diabetic patients.Metabolism. 2013 Dec;62(12):1858-66. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.08.008. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 24050270 Review.
-
Pleiotropic effects of ARB in metabolic syndrome.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2011 Mar;9(2):158-61. doi: 10.2174/157016111794519318. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21143168 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic AT1 blockade improves hyperglycemia by decreasing adipocyte inflammation and decreasing hepatic PCK1 and G6PC1 expression in obese rats.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Nov 1;321(5):E714-E727. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00584.2020. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34658252 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudocannabinoid H4CBD improves glucose response during advanced metabolic syndrome in OLETF rats independent of increase in insulin signaling proteins.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2024 Feb 1;326(2):R100-R109. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00125.2022. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2024. PMID: 37899754 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin receptor blockade with olmesartan alleviates brain pathology in obese OLETF rats.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2023 Mar;50(3):228-237. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13738. Epub 2022 Dec 4. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36398458 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

