Factor XII in inflammation and wound healing
- PMID: 29994899
- PMCID: PMC9377792
- DOI: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000450
Factor XII in inflammation and wound healing
Abstract
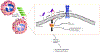
Purpose of review: This review describes the contribution of coagulation factor XII (FXII) in sterile inflammation and wound healing, focusing on recently identified roles for zymogen FXII in neutrophil functions.
Recent findings: Recent studies have identified an important role for FXII in neutrophil trafficking. In particular, following neutrophil activation, autocrine FXII signals through the urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) on the neutrophil surface to upregulate neutrophil functions. The sum of these activities leads to neutrophil adhesion, chemotaxis, and neutrophil extracellular (NET) formation. Downregulating FXII-mediated signaling in neutrophils is associated with improved wound healing.
Summary: These recent findings show the sophisticated role of FXII in vivo and create new opportunities for research on the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
None
Figures
References
-
- Larsson M, Rayzman V, Nolte MW, Nickel KF, Bjorkqvist J, Jamsa A, Hardy MP, Fries M, Schmidbauer S, Hedenqvist P, et al.: A factor XIIa inhibitory antibody provides thromboprotection in extracorporeal circulation without increasing bleeding risk. Sci Transl Med 2014, 6:222ra217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

