Electrophysiological characterisation of central sensitisation in canine spontaneous osteoarthritis
- PMID: 29994993
- PMCID: PMC6195806
- DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001336
Electrophysiological characterisation of central sensitisation in canine spontaneous osteoarthritis
Abstract
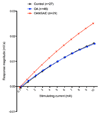
In man, central sensitisation (CS) contributes to the pain of osteoarthritis (OA). Dogs with spontaneous OA may also exhibit CS. Electrophysiological reflex measurements are more objective than behavioural assessments and can be used to evaluate CS in preclinical and clinical studies. It was hypothesised that dogs suffering from OA would exhibit electrophysiological characteristics indicative of CS, associated with reduced diffuse noxious inhibitory controls (DNICs). One hundred and seventeen client-owned dogs were recruited to the study. Hind limb nociceptive withdrawal reflex thresholds, stimulus response, and temporal summation characteristics were recorded, during alfaxalone anaesthesia, from 46 OA dogs, 29 OA dogs receiving nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (OANSAIDs), and 27 breed- and weight-matched control dogs. Efficacy of DNIC was evaluated in 12 control and 11 of the OA dogs, by application of a mechanical conditioning stimulus to the contralateral forelimb. Nociceptive withdrawal reflex thresholds were higher in OA compared with control dogs (P = 0.02). Stimulus response characteristics demonstrated an augmented response in OANSAID dogs compared with OA (P < 0.001) and control (P < 0.001) dogs. Temporal summation demonstrated exaggerated C-fibre-mediated responses in both OA (P < 0.001) and OANSAID (P = 0.005) groups, compared with control animals. Conditioning stimulus application resulted in inhibition of test reflex responses in both OA and control animals (P < 0.001); control animals demonstrated greater inhibition compared with OA (P = 0.0499). These data provide evidence of neurophysiological changes consistent with CS in dogs with spontaneous OA and demonstrate that canine OA is associated with reduced DNIC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Arendt-Nielsen L, Egsgaard LL, Petersen KK. Evidence for a central mode of action for etoricoxib (COX-2 inhibitor) in patients with painful knee osteoarthritis. Pain. 2016;157:1634–1644. - PubMed
-
- Arendt-Nielsen L, Nie H, Laursen MB, Laursen BS, Madeleine P, Simonsen OH, Graven-Nielsen T. Sensitization in patients with painful knee osteoarthritis. Pain. 2010;149:573–581. - PubMed
-
- Bannister K, Patel R, Goncalves L, Townson L, Dickenson AH. Diffuse noxious inhibitory controls and nerve injury: restoring an imbalance between descending monoamine inhibitions and facilitations. Pain. 2015;156:1803–1811. - PubMed
-
- Barnhart MD, Hubbell JAE, Muir WW. Evaluation of the analgesic properties of acepromazine maleate, oxymorphone, medetomidine and a combination of acepromazine-oxymorphone. Vet Anaes Analg. 2000;27:89–96. - PubMed
-
- Bars DL, Dickenson AH, Besson J-M. Diffuse noxious inhibitory controls (DNIC). II. Lack of effect on non-convergent neurones, supraspinal involvement and theoretical implications. Pain. 1979;6:305–327. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

