WDR41 supports lysosomal response to changes in amino acid availability
- PMID: 29995611
- PMCID: PMC6249801
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E17-12-0703
WDR41 supports lysosomal response to changes in amino acid availability
Abstract
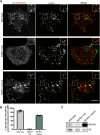
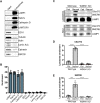
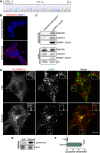
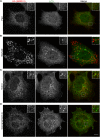
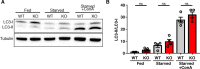
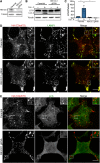
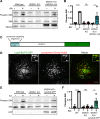
C9orf72 mutations are a major cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. The C9orf72 protein undergoes regulated recruitment to lysosomes and has been broadly implicated in control of lysosome homeostasis. However, although evidence strongly supports an important function for C9orf72 at lysosomes, little is known about the lysosome recruitment mechanism. In this study, we identify an essential role for WDR41, a prominent C9orf72 interacting protein, in C9orf72 lysosome recruitment. Analysis of human WDR41 knockout cells revealed that WDR41 is required for localization of the protein complex containing C9orf72 and SMCR8 to lysosomes. Such lysosome localization increases in response to amino acid starvation but is not dependent on either mTORC1 inhibition or autophagy induction. Furthermore, WDR41 itself exhibits a parallel pattern of regulated association with lysosomes. This WDR41-dependent recruitment of C9orf72 to lysosomes is critical for the ability of lysosomes to support mTORC1 signaling as constitutive targeting of C9orf72 to lysosomes relieves the requirement for WDR41 in mTORC1 activation. Collectively, this study reveals an essential role for WDR41 in supporting the regulated binding of C9orf72 to lysosomes and solidifies the requirement for a larger C9orf72 containing protein complex in coordinating lysosomal responses to changes in amino acid availability.
Figures

References
-
- Baba M, Hong SB, Sharma N, Warren MB, Nickerson ML, Iwamatsu A, Esposito D, Gillette WK, Hopkins RF, 3rd, Hartley JL, et al (2006). Folliculin encoded by the BHD gene interacts with a binding protein, FNIP1, and AMPK, and is involved in AMPK and mTOR signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA , 15552–15557. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker M, Mackenzie IR, Pickering-Brown SM, Gass J, Rademakers R, Lindholm C, Snowden J, Adamson J, Sadovnick AD, Rollinson S, et al (2006). Mutations in progranulin cause tau-negative frontotemporal dementia linked to chromosome 17. Nature , 916–919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

