Electromyographic analysis of hip and knee muscles during specific exercise movements in females with patellofemoral pain syndrome: An observational study
- PMID: 29995792
- PMCID: PMC6076041
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011424
Electromyographic analysis of hip and knee muscles during specific exercise movements in females with patellofemoral pain syndrome: An observational study
Abstract
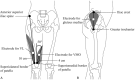
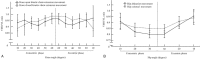
Hip muscle strengthening and knee extensor strengthening are common training exercises for patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS). PFPS engendered by insufficient hip abductor and external rotator muscle strength has been of interest, but these exercise movements may increase the lateral vector force of the patella warrants clarification. So, the purpose of this study was to assess muscular activations of vastus lateralis (VL), vastus medialis oblique (VMO), and gluteus medius muscles in electromyographic analysis during hip abduction and external rotator movements and open and closed kinetic chain knee extension movements.The gluteus medius, VMO, and VL muscles, in addition to the ratio of the VL and VMO muscles, were assessed through surface electromyography in 4 movements. Each muscle's amplitude expressed as a percent of maximum voluntary contraction (MVC). The differences on MVC at the terminal joint angle and during the movements were compared.Thirty female patients with PFPS were recruited. During hip abduction and external rotation movements, the MVC of the gluteus medius muscle increased, and those of the VMO and VL muscles increased in the open and closed kinetic chain knee extension movements. The MVCs of VL in the hip abduction and external rotation movements were significantly higher than those of the VMO muscle (P < .05). The ratios of the VL and VMO muscles in the open and closed kinetic chain knee extension movements approached 1, and they were significantly higher than those in the hip abduction and external rotation movements (P < .05). The highest MVC of the VMO muscle was observed at the terminal joint angle in the closed kinetic chain knee extension movement.Selective gluteus medius muscle activation was induced during the hip abduction and external rotation movements, accompanied by an increase in VL muscle activation. In open and closed kinetic chain knee movements, the ratios of the VL and VMO muscles approached 1. More selective VMO muscle activation was induced during the closed kinetic chain knee movements.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Vastus medialis obliquus and vastus lateralis activity in open and closed kinetic chain exercises in patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome: an electromyographic study.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001 Oct;82(10):1441-5. doi: 10.1053/apmr.2001.26252. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001. PMID: 11588751
-
Combining isometric knee extension exercises with hip adduction or abduction does not increase quadriceps EMG activity.Br J Sports Med. 2004 Apr;38(2):210-3. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2002.003277. Br J Sports Med. 2004. PMID: 15039261 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of closed-kinetic chain exercises and open-kinetic chain exercise on the muscle activity of vastus medialis oblique and vastus lateralis.J Strength Cond Res. 2010 May;24(5):1256-62. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181cf749f. J Strength Cond Res. 2010. PMID: 20386128 Clinical Trial.
-
Gluteus medius muscle activity in patellofemoral pain syndrome during squats: A Systematic Review.J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2024 Oct;40:1536-1543. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2024.03.007. Epub 2024 Apr 7. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2024. PMID: 39593485
-
Patellofemoral pain syndrome.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014 Oct;22(10):2264-74. doi: 10.1007/s00167-013-2759-6. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014. PMID: 24221245 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Core Training for Pain Management and Functional Improvement in Patients With Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2024 Dec 1;103(12):1094-1103. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000002513. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2024. PMID: 38684137 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Trigger Point Dry Needling on Neuromuscular Performance and Pain of Individuals Affected by Patellofemoral Pain: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Pain Res. 2020 Jul 7;13:1677-1686. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S240376. eCollection 2020. J Pain Res. 2020. PMID: 32753943 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Auxiliary Diagnostic Method for Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Based on One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network.Front Public Health. 2021 Apr 16;9:615597. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.615597. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33937165 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Gluteal Muscle Strengthening Exercise-Based Core Stabilization Training on Pain and Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Low Back Pain.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 May 23;60(6):849. doi: 10.3390/medicina60060849. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38929466 Free PMC article.
-
Surface Electromyography of the Vastus Lateralis, Biceps Femoris, and Gluteus Medius in Dogs During Stance, Walking, Trotting, and Selected Therapeutic Exercises.Front Vet Sci. 2019 Jul 10;6:211. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00211. eCollection 2019. Front Vet Sci. 2019. PMID: 31355214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohr KJ, Kvitne RS, Pink MM, et al. Electromyography of the quadriceps in patellofemoral pain with patellar subluxation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2003;415:261–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

