Resistance-gene-directed discovery of a natural-product herbicide with a new mode of action
- PMID: 29995859
- PMCID: PMC6097235
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0319-4
Resistance-gene-directed discovery of a natural-product herbicide with a new mode of action
Abstract
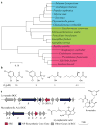
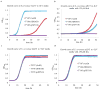
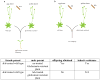
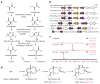
Bioactive natural products have evolved to inhibit specific cellular targets and have served as lead molecules for health and agricultural applications for the past century1-3. The post-genomics era has brought a renaissance in the discovery of natural products using synthetic-biology tools4-6. However, compared to traditional bioactivity-guided approaches, genome mining of natural products with specific and potent biological activities remains challenging4. Here we present the discovery and validation of a potent herbicide that targets a critical metabolic enzyme that is required for plant survival. Our approach is based on the co-clustering of a self-resistance gene in the natural-product biosynthesis gene cluster7-9, which provides insight into the potential biological activity of the encoded compound. We targeted dihydroxy-acid dehydratase in the branched-chain amino acid biosynthetic pathway in plants; the last step in this pathway is often targeted for herbicide development10. We show that the fungal sesquiterpenoid aspterric acid, which was discovered using the method described above, is a sub-micromolar inhibitor of dihydroxy-acid dehydratase that is effective as a herbicide in spray applications. The self-resistance gene astD was validated to be insensitive to aspterric acid and was deployed as a transgene in the establishment of plants that are resistant to aspterric acid. This herbicide-resistance gene combination complements the urgent ongoing efforts to overcome weed resistance11. Our discovery demonstrates the potential of using a resistance-gene-directed approach in the discovery of bioactive natural products.
Figures








Comment in
-
New routes to kill weeds.Nat Plants. 2018 Aug;4(8):509. doi: 10.1038/s41477-018-0227-5. Nat Plants. 2018. PMID: 30076397 No abstract available.
References
-
- Newman DJ, Cragg GM. Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J Nat Prod. 2016;79:629–661. - PubMed
-
- Jon C, Christopher W. Lessons from natural molecules. Nature. 2004;432:829–837. - PubMed
-
- Ziemert N, Alanjary M, Weber T. The evolution of genome mining in microbes - a review. Nat Prod Rep. 2016;33:988–1005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

