Propofol prevents human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury from Ang II-induced apoptosis by activating the ACE2-(1-7)-Mas axis and eNOS phosphorylation
- PMID: 29995907
- PMCID: PMC6040691
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199373
Propofol prevents human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury from Ang II-induced apoptosis by activating the ACE2-(1-7)-Mas axis and eNOS phosphorylation
Abstract
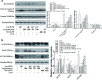
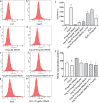
Angiotensin II (AngII), a vasoactive peptide that elevates arterial blood pressure and results in hypertension, has been reported to directly induce vascular endothelial cell apoptosis. Recent work has demonstrated that propofol pre-treatment attenuates angiotensin II-induced apoptosis in human coronary artery endothelial cells. However, the underlying mechanism remains largely unknown. Here, we investigated human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) subjected to angiotensin II-induced apoptosis in the presence or absence of propofol treatment and found that angiotensin II-induced apoptosis was attenuated by propofol in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, ELISA assays demonstrated that the ratio of angiotensin (1-7) (Ang (1-7)) to Ang II was increased after propofol treatment. We examined the expression of ACE2, Ang (1-7) and Mas and found that the ACE2-Ang (1-7)-Mas axis was up-regulated by propofol, while ACE2 overexpression increased phosphorylated endothelial nitric oxide synthase (phosphorylated eNOS) expression and siACE2 resulted in the repression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) phosphorylation. In conclusion, our study revealed that propofol can inhibit endothelial cell apoptosis induced by Ang II by activating the ACE2-Ang (1-7)-Mas axis and further up-regulating the expression and phosphorylation of eNOS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Zicha J, Kunes J. Ontogenetic aspects of hypertension development: analysis in the rat. Physiol Rev. 1999;79(4):1227–82. Epub 1999/10/03. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1999.79.4.1227 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Davignon J, Ganz P. Role of endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2004;109(23 Suppl 1):Iii27–32. Epub 2004/06/17. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000131515.03336.f8 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bader M, Ganten D. Update on tissue renin-angiotensin systems. J Mol Med (Berl). 2008;86(6):615–21. Epub 2008/04/17. doi: 10.1007/s00109-008-0336-0 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bader M. Tissue renin-angiotensin-aldosterone systems: Targets for pharmacological therapy. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010;50:439–65. Epub 2010/01/09. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.010909.105610 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang B, Shravah J, Luo H, Raedschelders K, Chen DD, Ansley DM. Propofol protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced injury in cardiac H9c2 cells via Akt activation and Bcl-2 up-regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;389(1):105–11. Epub 2009/08/26. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.08.097 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3631547. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

