Polar Lipids from Olives and Olive Oil: A Review on Their Identification, Significance and Potential Biotechnological Applications
- PMID: 29996479
- PMCID: PMC6068626
- DOI: 10.3390/foods7070109
Polar Lipids from Olives and Olive Oil: A Review on Their Identification, Significance and Potential Biotechnological Applications
Abstract
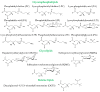
Polar lipids are minor components of olives and olive oil and include a myriad of molecules such as phospholipids and glycolipids. Even though sensitive and high-resolution analytical approaches have been used to unveil the polar lipidome of these matrices, new insights on their composition are needed. In this review, we will describe the findings on the identification and characterization of polar lipids from olives and olive oil and the underlying analytical challenges. The significance of polar lipids will also be discussed as potential markers of identity and traceability of olives and olive oil and in detecting adulteration of olive oil. Their potential impact on nutrition and health will be presented as a valuable source of bioactive compounds and as promising ingredients for different uses from olive-derived industrial by-products.
Keywords: authentication; bioactive; by-product; glycolipid; lipidomics; mass spectrometry; phospholipid; traceability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- International Olive Council World Olive Oil Figures. [(accessed on 18 December 2017)]; Available online: http://www.internationaloliveoil.org/estaticos/view/131-world-olive-oil-....
-
- Boskou D. 1-Olive oil: Properties and processing for use in food. In: Talbot G., editor. Specialty Oils and Fats in Food and Nutrition. 1st ed. Woodhead; Cambridge, UK: 2015. pp. 3–38.
-
- Servili M., Esposto S., Fabiani R., Urbani S., Taticchi A., Mariucci F., Selvaggini R., Montedoro G. Phenolic compounds in olive oil: Antioxidant, health and organoleptic activities according to their chemical structure. Inflammopharmacology. 2009;17:76–84. doi: 10.1007/s10787-008-8014-y. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

