Trend of HIV/AIDS for the last 26 years and predicting achievement of the 90-90-90 HIV prevention targets by 2020 in Ethiopia: a time series analysis
- PMID: 29996776
- PMCID: PMC6042262
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-018-3214-6
Trend of HIV/AIDS for the last 26 years and predicting achievement of the 90-90-90 HIV prevention targets by 2020 in Ethiopia: a time series analysis
Abstract
Background: HIV infection continues to be epidemic of public health importance with a prevalence of 1.1% and incidence of 0.33/1000 population having low-intensity mixed epidemic. Ethiopia has adopted the 90-90-90 by 2020 target but its progress was not yet assessed. Therefore, this study aimed to assess the trend of HIV infection for the last 26 years and to predict the achievements of the 90-90-90 target.
Methods: We used aggregates of HIV/AIDS indicator data from 1990 to 2016 of UNAIDS data bases. The data were analyzed with excel and STATA. The trend line that best fits the regression was drawn, annual change was estimated and future values of HIV detection rate, coverage of antiretroviral therapy and viral suppression indicators were predicted and compared with the 90-90-90 targets.
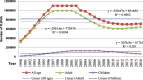
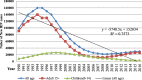
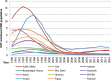
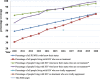
Result: Since 1995, new infection has declined by 81% and since 2002; number of HIV cases has declined by 35.5%. However, after remarkable decline for decades, since 2008 HIV incidence rate began to rise by 10% and number of new infection diagnosed each year increased by 36% among all ages and doubled among adults. ART coverage has increased by 90% among all age and tripled among pregnant women within 6 years. Nationally, 67% of people living with HIV know their status, 88% of them are on treatment and 86% of people on treatment have viral suppression. As a result, AIDS-related death declined by 77 and 79% among all age and children respectively. By 2020, 79% of people living with HIV will know their HIV status, of which 96-99% of HIV infected people will be on ART and more than 86% will have viral suppression.
Conclusion: After remarkable decline, HIV infection started to increase in the last few years among adults. With the current trend, Ethiopia will achieve the second and third 90% HIV targets, while the first target is not achievable and without achieving this overarching goal control of the epidemic will not be achieved. Therefore due attention is needed to avert the current epidemics and diagnosis of cases.
Keywords: Antiretroviral therapy; HIV/AIDS; The 90–90-90 target; Viral suppression.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). UNAIDS Data 2017. - PubMed
-
- Ethiopian public health institute. HIV related estimates and projections for Ethiopia–2017. Addis Ababa: Ethiopian public health institute; 2017.
-
- Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia. Country progress report on the HIV response. Addis Ababa: Minestery of health of ethiopia; 2014.
-
- UNAIDS. UNAIDS 90–90-90: an ambitious treatment target to help end the AIDS epidemic Geneva. Switzerland: World health organization; 2014.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

