Cationic liposomes induce cytotoxicity in HepG2 via regulation of lipid metabolism based on whole-transcriptome sequencing analysis
- PMID: 29996945
- PMCID: PMC6042442
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-018-0230-5
Cationic liposomes induce cytotoxicity in HepG2 via regulation of lipid metabolism based on whole-transcriptome sequencing analysis
Abstract
Backgroud: Cationic liposomes (CLs) can be used as non-viral vectors in gene transfer and drug delivery. However, the underlying molecular mechanism of its cytotoxicity has not been well elucidated yet.
Methods: We herein report a systems biology approach based on whole-transcriptome sequencing coupled with computational method to identify the predominant genes and pathways involved in the cytotoxicity of CLs in HepG2 cell line.
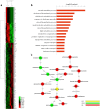
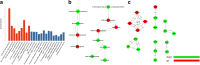
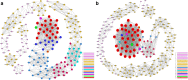
Results: Firstly, we validated the concentration-dependent cytotoxicity of CLs with an IC50 of 120 μg/ml in HepG2 exposed for 24 h. Subsequently, we used whole-transcriptome sequencing to identify 220 (77 up- and 143 down-regulated) differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Gene ontology (GO) and pathway analysis showed that these DEGs were mainly related to cholesterol, steroid, lipid biosynthetic and metabolic processes. Additionally, "key regulatory" genes were identified using gene act, pathway act and co-expression network analysis, and expression levels of 11 interested altered genes were confirmed by quantitative real time PCR. Interestingly, no cell cycle arrest was observed through flow cytometry.
Conclusions: These data are expected to provide deep insights into the molecular mechanism of CLs cytotoxicity.
Keywords: Cationic liposomes; Cytotoxicity; Lipid metabolism; Nanoparticle; RNA-seq.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Metabolomics revealed the toxicity of cationic liposomes in HepG2 cells using UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS and multivariate data analysis.Biomed Chromatogr. 2017 Dec;31(12). doi: 10.1002/bmc.4036. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Biomed Chromatogr. 2017. PMID: 28664536
-
Identification of Genes Related to Growth and Lipid Deposition from Transcriptome Profiles of Pig Muscle Tissue.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 27;10(10):e0141138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141138. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26505482 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Transcriptome Analysis of CD36 Overexpression in HepG2.2.15 Cells to Explore Its Regulatory Role in Metabolism and the Hepatitis B Virus Life Cycle.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 17;11(10):e0164787. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164787. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27749922 Free PMC article.
-
Development of glycyrrhetinic acid-modified stealth cationic liposomes for gene delivery.Int J Pharm. 2010 Sep 15;397(1-2):147-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2010.06.029. Epub 2010 Jul 27. Int J Pharm. 2010. PMID: 20667672
-
RNA-Seq provides new insights in the transcriptome responses induced by the carcinogen benzo[a]pyrene.Toxicol Sci. 2012 Dec;130(2):427-39. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfs250. Epub 2012 Aug 13. Toxicol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22889811
Cited by
-
Resolvin D1-loaded nanoliposomes promote M2 macrophage polarization and are effective in the treatment of osteoarthritis.Bioeng Transl Med. 2022 Mar 7;7(2):e10281. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10281. eCollection 2022 May. Bioeng Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35600665 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosomes: Intrinsically Mucoadhesive Glycosylated Mucin Nanoparticles as Multi-Drug Delivery Platform.Adv Healthc Mater. 2022 Aug;11(15):e2200340. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202200340. Epub 2022 Jun 4. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022. PMID: 35608152 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Dose Intravenous Administration of Neutral and Cationic Liposomes in Mice: An Extensive Toxicity Study.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jun 18;15(6):761. doi: 10.3390/ph15060761. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35745680 Free PMC article.
-
Permanently Charged Cationic Lipids-Evolution from Excipients to Therapeutic Lipids.Small Sci. 2024 Jun 11;4(7):2300270. doi: 10.1002/smsc.202300270. eCollection 2024 Jul. Small Sci. 2024. PMID: 40212121 Free PMC article.
-
Promising strategies employing nucleic acids as antimicrobial drugs.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Jan 18;35(1):102122. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102122. eCollection 2024 Mar 12. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 38333674 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kargul J, Irminger-Finger ILaurent GJ, Nanomedicine: Application of nanoparticles in clinical therapies and diagnostics[J]. International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. 2016;75(140-. - PubMed
-
- Schmitt-Sody M, Strieth S, Krasnici S, Sauer B, Schulze B, Teifel M, Michaelis U, Naujoks KDellian M. Neovascular targeting therapy: paclitaxel encapsulated in cationic liposomes improves antitumoral efficacy[J] Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(6):2335–2341. - PubMed
-
- Baker R. Early approval for two lipid-based drugs[J]. BETA. 1995;4 - PubMed
-
- FDA approves DaunoXome as first-line therapy for Kaposi's sarcoma. Food and Drug Administration[J]. J Int Assoc Physicians AIDS Care. 1996;2(5):50–1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

