Therapeutic Targeting of KDM1A/LSD1 in Ewing Sarcoma with SP-2509 Engages the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response
- PMID: 29997151
- PMCID: PMC6201274
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0373
Therapeutic Targeting of KDM1A/LSD1 in Ewing Sarcoma with SP-2509 Engages the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response
Abstract
Multi-agent chemotherapeutic regimes remain the cornerstone treatment for Ewing sarcoma, the second most common bone malignancy diagnosed in pediatric and young adolescent populations. We have reached a therapeutic ceiling with conventional cytotoxic agents, highlighting the need to adopt novel approaches that specifically target the drivers of Ewing sarcoma oncogenesis. As KDM1A/
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Stephen L. Lessnick is a consultant/advisory board member for Salarius Pharmaceuticals. Sunil Sharma is a founder and has equity in Salarius Pharmaceuticals
Figures
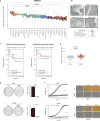

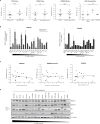
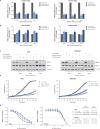
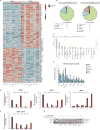
References
-
- Delattre O, Zucman J, Plougastel B, Desmaze C, Melot T, Peter M, et al. Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature. 1992;359(6391):162–5. - PubMed
-
- Sorensen PH, Lessnick SL, Lopez-Terrada D, Liu XF, Triche TJ, Denny CT. A second Ewing’s sarcoma translocation, t(21;22), fuses the EWS gene to another ETS-family transcription factor, ERG. Nature genetics. 1994;6(2):146–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

