Epstein-Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen 3C Facilitates Cell Proliferation by Regulating Cyclin D2
- PMID: 29997218
- PMCID: PMC6146702
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00663-18
Epstein-Barr Virus Nuclear Antigen 3C Facilitates Cell Proliferation by Regulating Cyclin D2
Abstract
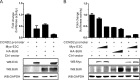
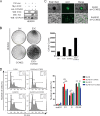
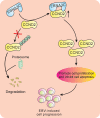
Cell cycle regulation is one of the hallmarks of virus-mediated oncogenesis. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-induced lymphomas express a repertoire of essential viral latent proteins that regulate expression of cell cycle-related proteins to dysregulate this process, thereby facilitating the proliferation of infected cells. We now demonstrate that the essential EBV latent protein 3C (EBNA3C) stabilizes cyclin D2 to regulate cell cycle progression. More specifically, EBNA3C directly binds to cyclin D2 and they colocalize together in nuclear compartments. We show that EBNA3C regulates the promoter of cyclin D2 through cooperation with master transcription factor Bcl6 and enhances its stability by inhibiting its ubiquitin-dependent degradation. EBNA3C also promoted cell proliferation in the presence of cyclin D2, suggesting that cyclin D2 contributes to EBNA3C-mediated cell cycle progression. These results provide new clues as to the role of this essential viral latent protein and its ability to regulate expression of cellular factors, which drives the oncogenic process.IMPORTANCE Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is the first identified human tumor virus and is associated with a range of human cancers. During EBV-induced lymphomas, the essential viral latent proteins modify the expression of cell cycle-related proteins to disturb the cell cycle process, thereby facilitating the proliferative process. The essential EBV nuclear antigen 3C (EBNA3C) plays an important role in EBV-mediated B-cell transformation. Here we show that EBNA3C stabilizes cyclin D2 to regulate cell cycle progression. More specifically, EBNA3C directly binds to cyclin D2, and they colocalize together in nuclear compartments. EBNA3C enhances cyclin D2 stability by inhibiting its ubiquitin-dependent degradation and significantly promotes cell proliferation in the presence of cyclin D2. Our results provide novel insights into the function of EBNA3C on cell progression by regulating the cyclin D2 protein and raise the possibility of the development of new anticancer therapies against EBV-associated cancers.
Keywords: EBNA3C; Epstein-Barr virus; cell proliferation; cyclin D2.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EBNA3C facilitates RASSF1A downregulation through ubiquitin-mediated degradation and promoter hypermethylation to drive B-cell proliferation.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Jan 7;15(1):e1007514. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007514. eCollection 2019 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30615685 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 3C regulates cyclin A/p27 complexes and enhances cyclin A-dependent kinase activity.J Virol. 2004 Feb;78(4):1981-91. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.4.1981-1991.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14747563 Free PMC article.
-
The F-box E3 ligase protein FBXO11 regulates EBNA3C-associated degradation of BCL6.J Virol. 2024 Jul 23;98(7):e0054824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00548-24. Epub 2024 Jun 12. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38864622 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein Barr nuclear antigen EBNA3C regulates transcription, cell transformation and cell migration.Front Biosci. 2002 Mar 1;7:d704-16. doi: 10.2741/subraman. Front Biosci. 2002. PMID: 11861219 Review.
-
Nucleoside diphosphate kinase/Nm23 and Epstein-Barr virus.Mol Cell Biochem. 2009 Sep;329(1-2):131-9. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0123-4. Epub 2009 May 3. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19412732 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted Therapies for Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Lymphomas.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 9;12(9):2565. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092565. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32916819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EBV and Lymphomagenesis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 4;15(7):2133. doi: 10.3390/cancers15072133. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitin-Mediated Effects on Oncogenesis during EBV and KSHV Infection.Viruses. 2024 Sep 26;16(10):1523. doi: 10.3390/v16101523. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39459858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CVB3 VP1 interacts with MAT1 to inhibit cell proliferation by interfering with Cdk-activating kinase complex activity in CVB3-induced acute pancreatitis.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Feb 8;17(2):e1008992. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008992. eCollection 2021 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33556114 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the links between neurodegeneration and Epstein-Barr virus-mediated cell cycle dysregulation.Curr Res Neurobiol. 2022 Jun 30;3:100046. doi: 10.1016/j.crneur.2022.100046. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 36685766 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Epstein MA, Achong BG, Barr YM. 1964. Virus particles in cultured lymphoblasts from Burkitt's lymphoma. Lancet i:702–703. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

