Gene by Culture Effects on Emotional Processing of Social Cues among East Asians and European Americans
- PMID: 29997310
- PMCID: PMC6070862
- DOI: 10.3390/bs8070062
Gene by Culture Effects on Emotional Processing of Social Cues among East Asians and European Americans
Abstract
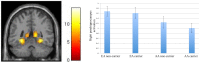
While Western cultures are more focused on individualization and self-expression, East Asian cultures promote interrelatedness. Largely unknown is how gene by culture interactions influence the degree to which individuals acquire culture, and the neurocircuitry underlying how social cues are processed. We sought to examine the interaction between DRD4 polymorphism and culture in the neural processing of social emotional cues. 19 Asian-born East Asian (AA) and 20 European American (EA) participants performed a shifted attention emotion appraisal functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) task, which probes implicit emotional processing and regulation in response to social emotional cues. Half of the participants in each group were DRD4 2- or 7-repeat allele (2R/7R) carriers. AA participants showed larger left and right amygdala, and left hippocampal activation during implicit processing of fearful faces. There was a gene by culture interaction in the left insula during implicit processing of facial cues, while activation in EA DRD4 2R/7R carriers was larger than EA non-carriers and AA carriers. Our findings suggest that emotional facial cues are more salient to AA participants and elicit a larger amygdala reaction. Gene by culture interaction finding in insula suggests that DRD4 2R/7R carriers in each culture are more prone to adopting their cultural norm.
Keywords: amygdala; culture; emotion; gene; insula; social.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
DRD4 polymorphisms modulate reward positivity and P3a in a gambling task: Exploring a genetic basis for cultural learning.Psychophysiology. 2020 Oct;57(10):e13623. doi: 10.1111/psyp.13623. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Psychophysiology. 2020. PMID: 32583892
-
Increased brain activity to unpleasant stimuli in individuals with the 7R allele of the DRD4 gene.Psychiatry Res. 2015 Jan 30;231(1):58-63. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2014.10.021. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Psychiatry Res. 2015. PMID: 25481571 Free PMC article.
-
Self-construal differences in neural responses to negative social cues.Biol Psychol. 2017 Oct;129:62-72. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2017.07.023. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Biol Psychol. 2017. PMID: 28782584
-
[Processing mechanism of social cues in faces].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2019 Feb 25;71(1):73-85. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 30778506 Review. Chinese.
-
Distributed and interactive brain mechanisms during emotion face perception: evidence from functional neuroimaging.Neuropsychologia. 2007 Jan 7;45(1):174-94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2006.06.003. Epub 2006 Jul 18. Neuropsychologia. 2007. PMID: 16854439 Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping Cultural Values onto the Brain: the Fragmented Landscape.Integr Psychol Behav Sci. 2024 Dec;58(4):1434-1479. doi: 10.1007/s12124-020-09553-0. Integr Psychol Behav Sci. 2024. PMID: 32495163
-
Non-suicidal self-injury in adolescents with mood disorders and the roles of self-compassion and emotional regulation.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Dec 21;14:1214192. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1214192. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 38179248 Free PMC article.
-
Facilitators and Barriers to Physical Activity for Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis and Axial Spondyloarthritis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2025 Feb;28(2):e70109. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.70109. Int J Rheum Dis. 2025. PMID: 39895470 Free PMC article.
-
Practical approaches to conducting biopsychosocial research with refugee and internally displaced communities.Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2023 Nov 7;16:100217. doi: 10.1016/j.cpnec.2023.100217. eCollection 2023 Nov. Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2023. PMID: 38108032 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Psychiatry in Displaced Populations: What We Know, and What We Need to Begin to Learn.Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2022 Dec;7(12):1242-1250. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2022.05.001. Epub 2022 May 14. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2022. PMID: 35580738 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Markus H.R., Kitayama S. Culture and the self: Implications for cognition, emotion, and motivation. Psychol. Rev. 1991;98:224–253. doi: 10.1037/0033-295X.98.2.224. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

