Nipple sparing mastectomy and the evolving direct to implant breast reconstruction
- PMID: 29998076
- PMCID: PMC6006025
- DOI: 10.21037/gs.2017.08.06
Nipple sparing mastectomy and the evolving direct to implant breast reconstruction
Abstract
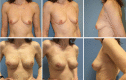
In this paper, we describe the evolving use of the nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) and direct to implant breast reconstruction according to existing literature and our own experience. The surgical method enables superior aesthetic results resembling that of a natural breast while maintaining oncologic safety. Acellular dermal matrix enables direct to implant breast reconstruction by serving as a hammock and can be used with acceptable rates of complications. A successful nipple-sparing mastectomy and direct to implant breast reconstruction approach with acceptable postoperative complication rates relies upon quality of the mastectomy skin flaps and correct patient selection. The surgical method has developed with a rapid pace and expected to evolve further in terms of technical modalities, safety measure and lasting results.
Keywords: Nipple sparing mastectomy (NSM); direct to implant (DTI); immediate breast reconstruction (IBR).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources