The Infection Process of Yersinia ruckeri: Reviewing the Pieces of the Jigsaw Puzzle
- PMID: 29998086
- PMCID: PMC6028603
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00218
The Infection Process of Yersinia ruckeri: Reviewing the Pieces of the Jigsaw Puzzle
Abstract
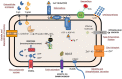
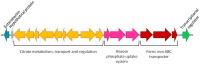
Finding the keys to understanding the infectious process of Yersinia ruckeri was not a priority for many years due to the prompt development of an effective biotype 1 vaccine which was used mainly in Europe and USA. However, the gradual emergence of outbreaks in vaccinated fish, which have been reported since 2003, has awakened interest in the mechanism of virulence in this pathogen. Thus, during the last two decades, a large number of studies have considerably enriched our knowledge of many aspects of the pathogen and its interaction with the host. By means of both conventional and a variety of novel strategies, such as cell GFP tagging, bioluminescence imaging and optical projection tomography, it has been possible to determine three putative Y. ruckeri infection routes, the main point of entry for the bacterium being the gill lamellae. Moreover, a wide range of potential virulence factors have been highlighted by specific gene mutagenesis strategies or genome-wide transposon/plasmid insertion-based screening approaches, such us in vivo expression technology (IVET) and signature tagged mutagenesis (STM). Finally, recent proteomic and whole genomic analyses have allowed many of the genes and systems that are potentially implicated in the organism's pathogenicity and its adaptation to the host environmental conditions to be elucidated. Altogether, these studies contribute to a better understanding of the infectious process of Y. ruckeri in fish, which is crucial for the development of more effective strategies for preventing or treating enteric redmouth disease (ERM).
Keywords: Yersinia ruckeri; comparative genome; infection route; proteome analysis; virulence genes.
Figures

References
-
- Amend D. F., Johnson K. A., Croy T. R., McCarthy D. H. (1983). Some factors affecting the potency of Yersinia ruckeri bacterins. J. Fish Dis. 6, 337–344.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

